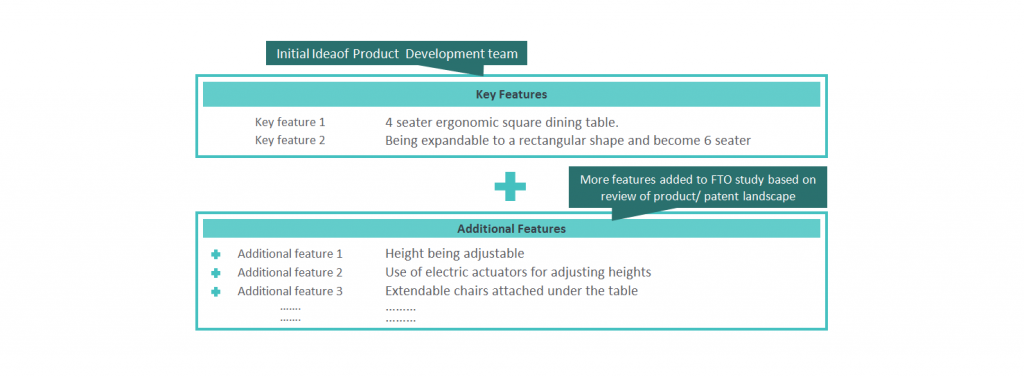
Decades ago, green or sustainable coatings were termed eco-friendly coatings that emit almost negligible volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the production process. But now, this definition has been extended to include aspects of sustainability. Today, companies are also looking to impact the entire value chain and consider the societal impacts of their activities.
Three major elements are driving the coating industry towards sustainability: Health, Climate Change, and the Circular Economy. These entail energy and resource conservation, waste minimization, process efficiency enhancement, the use of renewable materials, and much more.
With the growing concerns for climate and sustainability, we can expect these practices to give birth to more innovations and products soon. To get an idea of the same, we researched the top innovation trends in the Industry. In this article, we’ll dig into these trends. But first, let’s see how the industry is growing.
We have also converted this long article into a PDF. If you want the pdf, fill out the form below:
Expected growth in market size of the industry and the reasons behind it
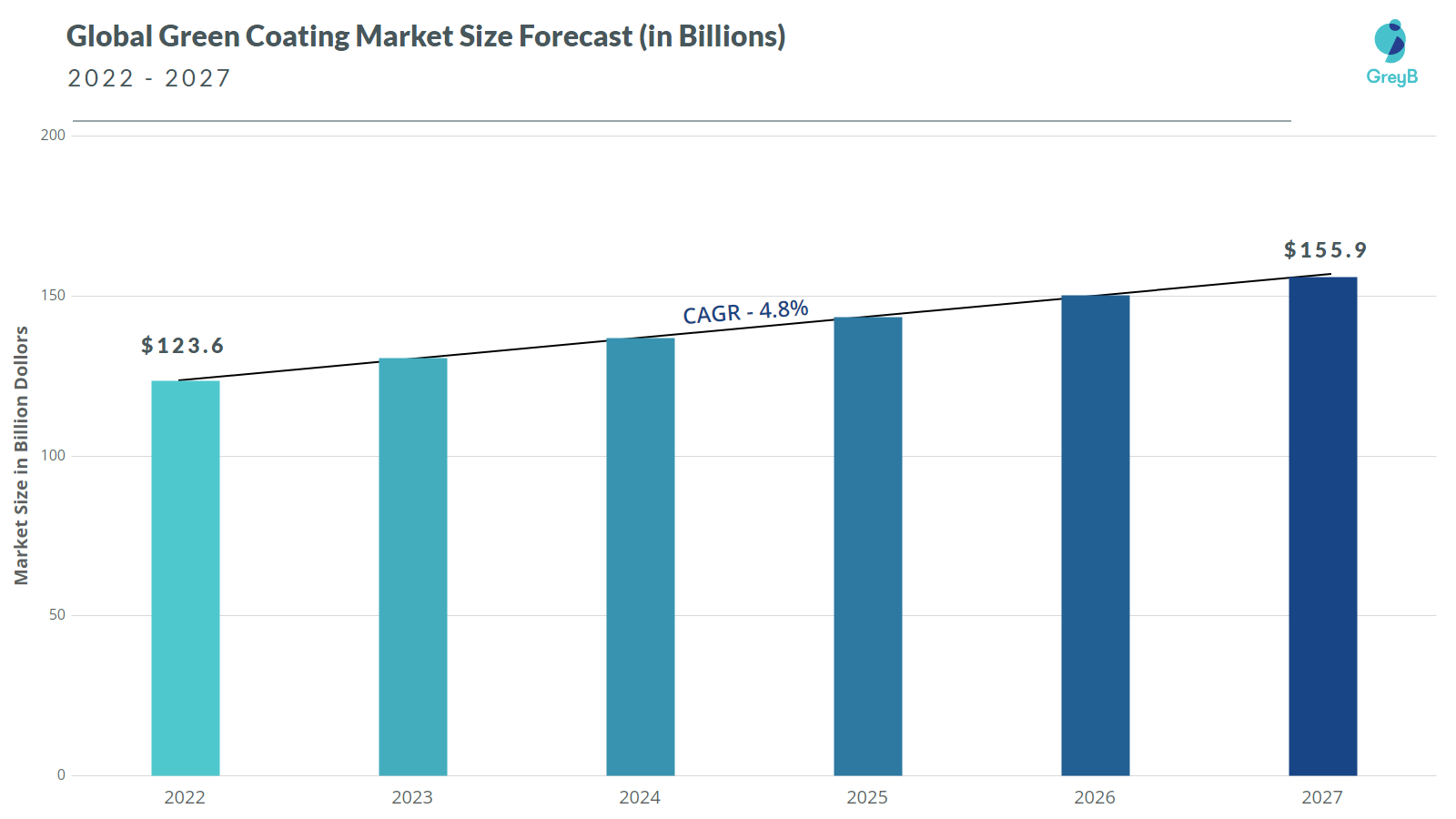
The global green coating market was valued at $123.6 Billion in 2022. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2022 to 2027 and reach $155.9 billion in 2027. (Source)
Possible reasons for this growth –
- The construction and automotive sectors have witnessed a consistently growing product penetration and exponential product and innovation growth.
- The climate concerns and public awareness are pushing the existing OEMs as well as start-ups and small businesses to innovate and develop more eco-friendly coating.
- The increase in demand could also be attributed to the company’s willingness to replace the existing coatings with low-VOC emitting coatings.
- An increase in stringent government regulations associated with VOC.
- There’s rising demand for waterborne and powder technology, especially in architectural and automotive applications, which is also expected to drive industry growth. (Source, Source)
Sustainable Coatings Trends
To understand the trends in “Sustainable Coating”, we would be starting with three major verticals –
- Methods of Sustainable Coating,
- Materials for Sustainable Coating, and
- Applications of Sustainable Coating.

Note: In each vertical, we conducted an in-depth study of its types and the parameters associated with the market and patent statistics to predict which aspects would gain traction soon.
Coating Methods
1. Powder Coating
Powdered polymer resins are melted, mixed, cooled, and grounded in uniform powder (like baking flour). Powder coatings contain no solvents and therefore emit negligible polluting VOCs into the atmosphere. 1,2
2. High Solids’ Coating
It is a single or dual coating formulated with higher concentrations (at least 65%) of solids (binders, pigments, and additives) despite a lower percentage of VOCs. They are more environmentally friendly because less solvent is emitted as it dries or cures. 1
3. UV-Cure Coating
It is a kind of radiation cure coating that offers rapid drying time, low energy consumption (hence less energy cost), fewer VOC emissions, reduced floor space requirements, and an indefinite pot life. 1
4. Waterborne Coating
It is an eco-friendly surface treatment that uses water as a solvent to disperse the resins used in coating: They have low VOC content, high corrosion protection, less toxicity and flammability, and thus, are eco-friendly. 1
5. Radiation Cure Coating
They are cross-linked or cured using high-intensity radiation energy from electron beams or ultraviolet light radiation. They utilize less energy, hence require low energy costs and exhibit improved corrosion protection for metals. (Source)
6. Solvent-less Coating
This kind of fluid is applied to a substrate’s surface to prevent corrosion. It has an impermeable preventative layer with low or no moisture content. The layer helps reduce an electrolytic attack on the metal’s surface. 1
Other minor methods of sustainable or green coating are – solar reflective coating, chrome-free coating, bio-renewable coating, etc. (Source)
Which Coating Methods have been dominating the Market?
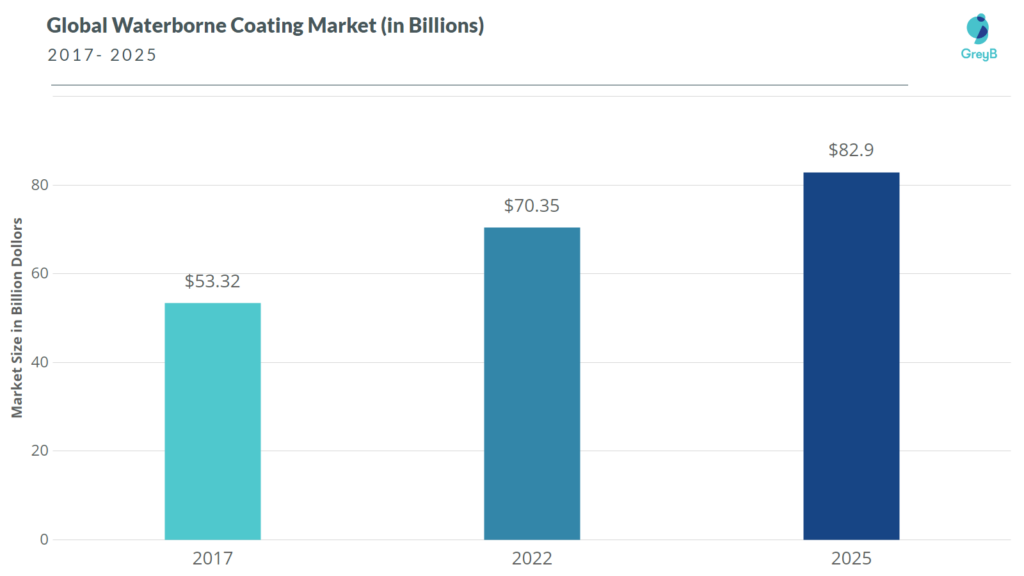
The global waterborne coating market, which was valued at $53.32 billion in 2017, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.7% from 2017 to 2025 and reach $82.9 billion by 2025. (1, 2)
The global powder coating market, which was valued at $11.9 billion in 2020, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2020 to 2028 and reach $20.8 billion by 2028. (1, 2)
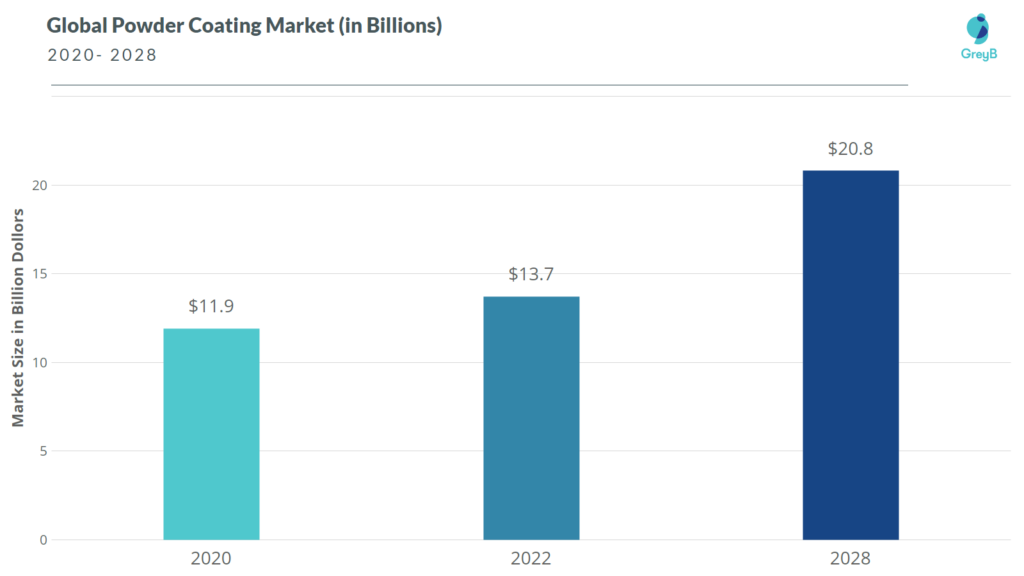
The global radiation cure coating market, which was valued at $8.76 billion in 2020, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2020 to 2024 and reach $11.4 billion by 2024. (1)
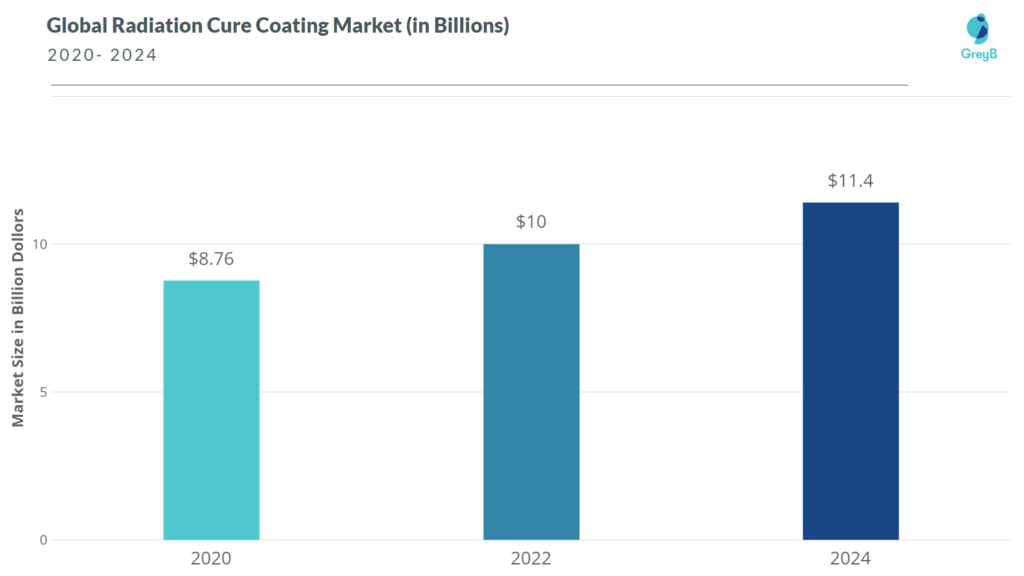
The global high solids’ coating market, which was valued at $10.01 billion in 2016, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2017 to 2025 and reach $17.8 billion by 2025. (1)
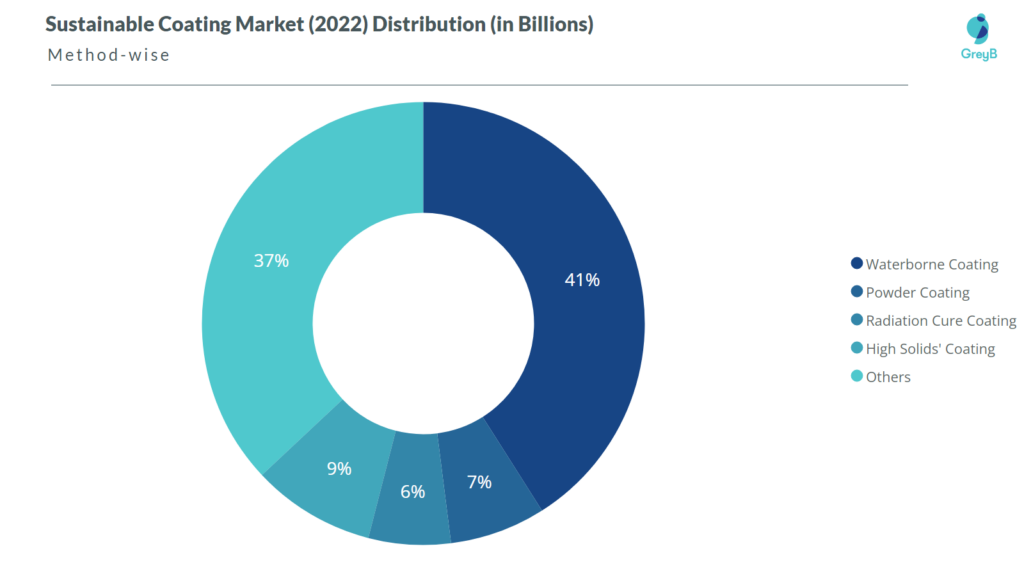
The market size of Sustainable Coatings in 2022 is expected to be$171 Billion.
As per our analysis, the Sustainable Coating market of 2022 would be divided into the following segments based on methods.
Around which methods is the maximum innovation centered?
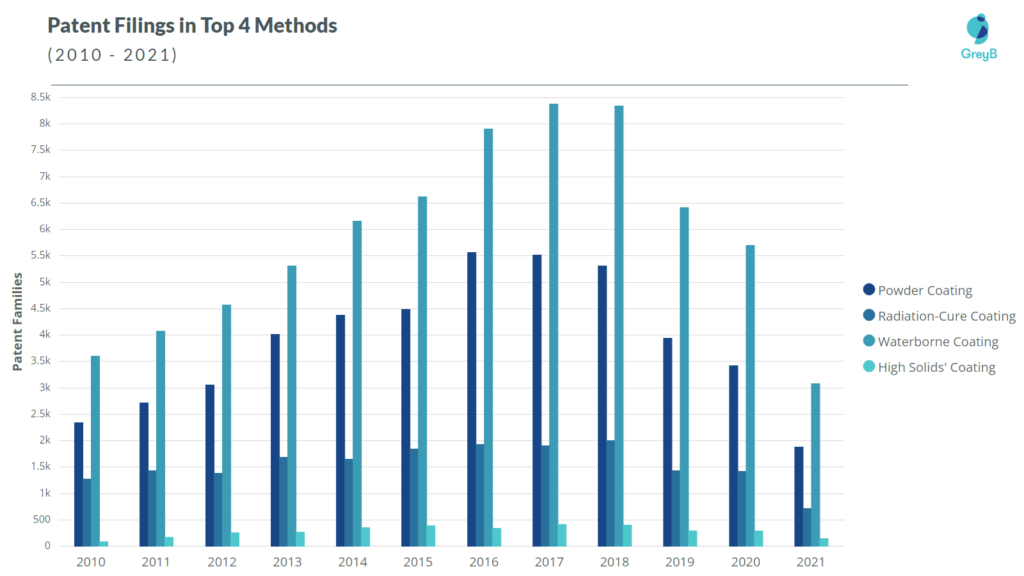
The following bar graph is plotted between the patent count and the application year of each patent. Please note that to study comprehensively the application years, we have taken each member of the patent family as a separate entity.
- The CAGR of patent filing from 2010 to 2018 in the four methods are as follows –
- Waterborne Coating – 11%
- Powder Coating – 11%
- Radiation-cure Coating – 6%
- High Solids’ Coating – 22%
- Observing the CAGR, we can say that dry coating techniques are gaining traction whereas forms like solvent-based coating are getting obsolete due to their non-sustainable nature.
- In terms of volume (number) of innovations, however, the total number of patents filed in the waterborne coating section in the past 11 years is almost equivalent to the sum of patent-filing in dry-coating – High Solids and Powder coating.
- High solids coating is being widely used in the aerospace industry and other industries as a way to comply with the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) emissions regulations. This is one major reason attributed to the drastic growth in the patent filing in High Solids’ Coating. 1
Waterborne coating is having a greater market (current and predicted), the highest volume, and the maximum rate of patents filed in the sustainable coating section. This is attributed to its highly sustainable nature and an easy shift from non-sustainable solvent-based to sustainable waterborne coatings.
We believe that the rate of innovation and development would also increase in dry coating techniques, including Powder and High Solids’ Coating. This is because, in addition to the sustainability considerations, there is a strong deviation of the business ecosystem towards water-conservation practices. * – Source1 and Source2
What are the different materials used for making coatings sustainable?
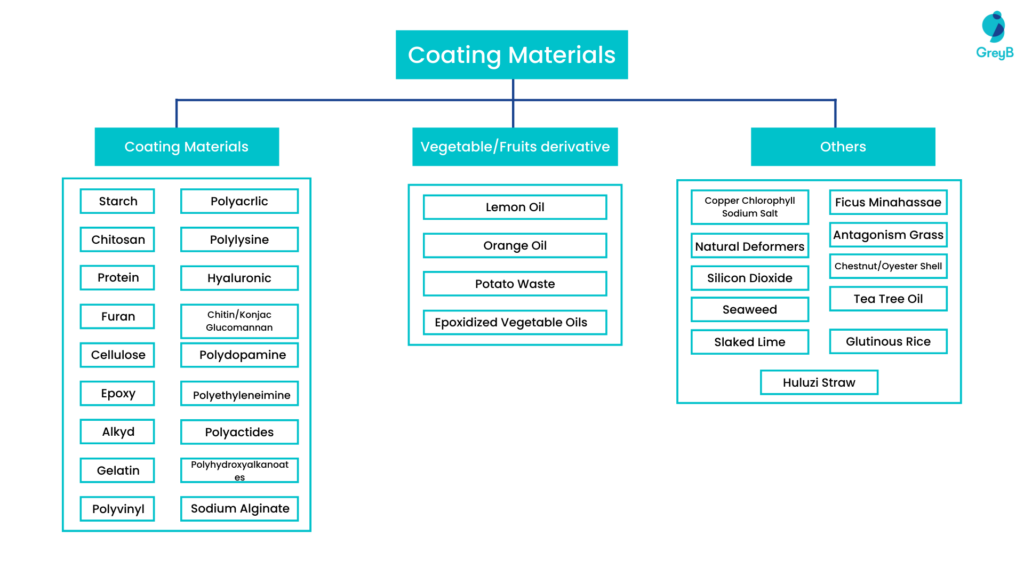
Coating materials can be produced from polymeric materials such as Starch, Protein, and Cellulose. It can also be derived from fruits and vegetables and other materials like seaweed, slaked lime, etc.
Below are described properties of a few materials that can be used for sustainable coating.
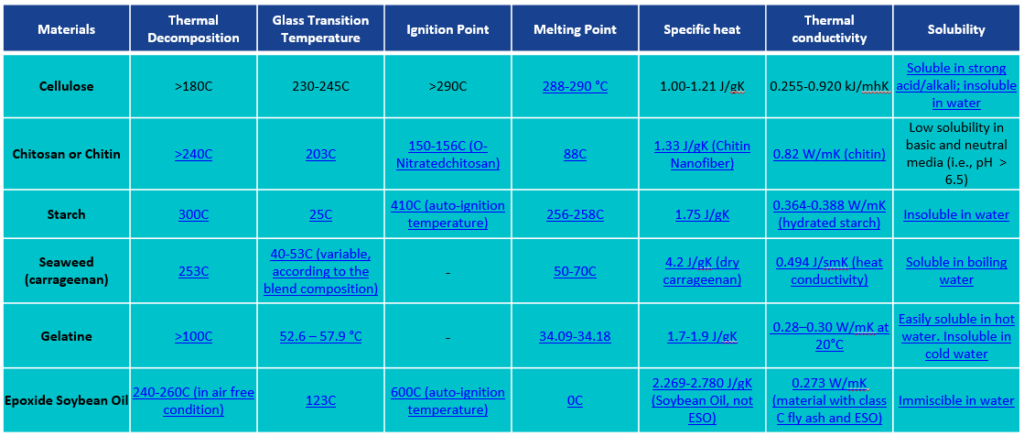
Let’s take Cellulose as an example, as it is the most abundant element on the earth and, thus, the cheapest to procure. When compared with other similar materials (abundant earth materials), cellulose is found to have the highest melting point and glass transition temperature. This makes it the best fit for coating products. Moreover, it is not soluble in water and has a balanced range of parameters that make cellulose the desired choice for sustainable coatings.
Let’s look into the properties of Cellulose
- Cellulose is a non-toxic, biodegradable solid, the most abundant element on the earth and the main component of all plants.
- It has excellent properties such as high hardness, high strength, high crystallinity, large surface tension, high resistivity (low conductivity), and special properties of nanoparticles. Due to these, the polymer barrier properties, thermal properties, and mechanical properties can be improved when it is incorporated into the coating.
- Cellulose is completely safe to eat, and this edibility makes it a suitable eco-friendly material for coatings.
- Cellulose represents approximately 1,500 Giga-tons (1,500,000,000,000 tons) of annual biomass production. Utilizing biomass would not only be organic but would also help maintain a circular economy and optimize waste management. (Source)

What are the market prospects and opportunities in “Cellulose Coating”?
The global cellulose coating market was valued at $1.7 billion in 2020. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2020 to 2027 and reach $2.45 billion in 2027. (Source)
Market size in 2022 – $ 1.88 billion (estimated)
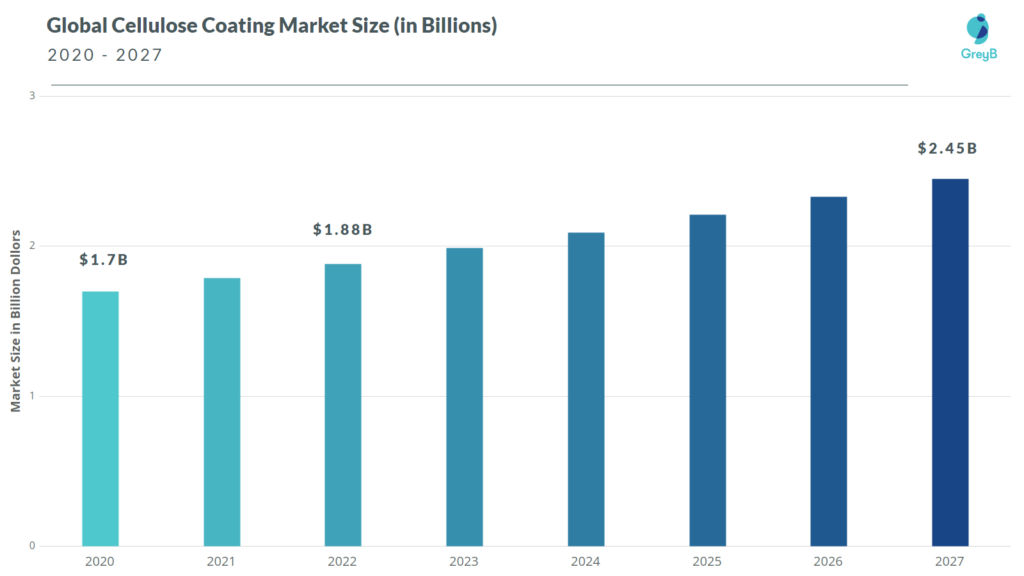
Prominent features of the cellulose coating market
- Due to increased construction activities, wood coating with cellulose nitrate has gained traction. 1
- Region-wise, Asia-Pacific topped the market by acquiring a 36.8% share in 2020.
- Cellulose is the most abundant material on the earth’s surface. Therefore, in the shift of the coating industry towards sustainability, cellulose would be a major game player.
- Research on cellulose in the coatings segment would also be complemented by research on cellulose in edible packaging and edible labels segment. For instance, If a solution to any prevailing problem is suggested in one of these three domains, it would be easily integrated into the other two as well.

The cellulose coating market comprises 9.6 % of the world’s cellulose and only 1.1 % of the world’s coating market as of 2022. However, out of the total patents in sustainable coatings that we analyzed, approximately 20% of them had mentioned cellulose in their composition.
This signifies that entities are heavily researching and filing patents in cellulose-based coatings. Cellulose would likely be a dominant ingredient and the torch-bearer in the upcoming “Sustainable Coating” revolution!
Are there any major interesting innovations centered around cellulose?
- EMPA Sustainable and Edible Coating
Generally in supermarkets, a lot of plastic waste is generated due to plastic packaging in fruits and vegetables. Also, non-packaged or uncovered fruits have a greater chance of getting rotten early.
A team of researchers from the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa) has found a solution to this problem by actually replacing plastic packaging with sustainable and edible coating. They have developed an invisible, edible, plant-based coating that can help fresh produce last longer — all the while taking plastic packaging out of the equation. Their coating has been created by using “pomace” — a pulpy residue left over from the blending of fruits and vegetables for juice.
They have developed a process where they could extract the cellulose that is naturally contained in these vegetables that can not otherwise be sold. By spraying the cellulose onto produce like cucumbers or bananas, it creates an additional layer of protection, slowing down moisture loss and oxidation. (Source)

- Moscow Power Institute coating based on bacterial cellulose
Mechanical damage to the liver is one of the most prominent and commonly occurring organ injuries. Some of the compositions to accelerate wound healing and tissue regeneration consist of polypeptides, nucleic acids, and suitable carriers. The disadvantage of these solutions is the possibility of rejection of materials due to the present antigenicity, especially when using biomaterials of animal origin.
Moscow Power Institute has patented (RU2695066C1) a solution for this problem by treating traumatic liver breaks using a film coating based on bacterial cellulose. This cellulose, when modified with animal proteins, is biologically compatible with the tissues of the human body and can regenerate damaged tissue.
This invention expands the range of drugs for the rapid recovery of the damaged organ.
- Surfresca breathable coating
Surfresca, founded in 2020 and headquartered in Israel, has developed a breathable coating, an edible, biodegradable, water-based emulsion composed of wholly natural food ingredients and built with advanced modified atmosphere properties.
When the coating is applied to fresh fruit or vegetables, the solution creates a breathable coating, with minute disruptions within the coating acting as a partial barrier, allowing for “optimal gas exchange.” This slows down the post-harvest maturation and ripening processes and subsequent degradation and decay. According to Surfresca, the sustainable solution could extend shelf-life by several weeks. (Source)
Most cellulose-based sustainable coating methods are associated with – edibles, cooking utensils, tablets and capsules, medical adhesive tape, eco-friendly fertilizers, or water-based fireproof heat insulation.
We believe that the Pharmaceutical, packed-food, and household utilities industries would be major markets demanding edible coating products like cellulose, which would open up various business opportunities.
In addition, cellulose might also witness an increased demand in novel areas like superhydrophobic coatings.
Applications of Sustainable Coating
Coatings can be used in many objects, products, and services worldwide. Their utility can be decorative, functional, or both. Functional coatings may be applied to change the substrate’s surface properties, such as adhesion, wettability, corrosion resistance, or wear resistance. Whereas, in the case of semiconductor device fabrication (where the substrate is a wafer), the coating adds a completely new property, such as a magnetic response or electrical conductivity, and forms an essential part of the finished product. (Source)
Let us have a look at the industrial and residential usages of coatings to get a brief about which markets have the highest opportunities for expanding the green coating industry –
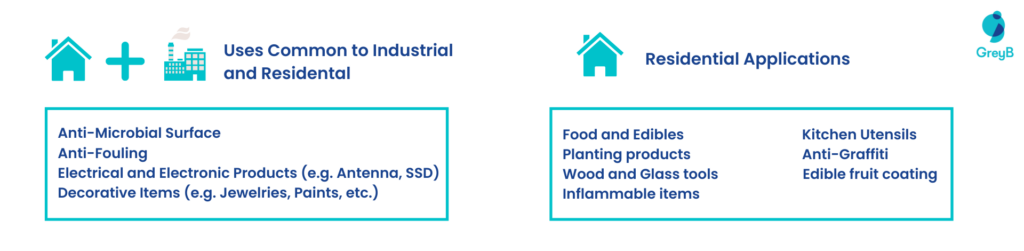
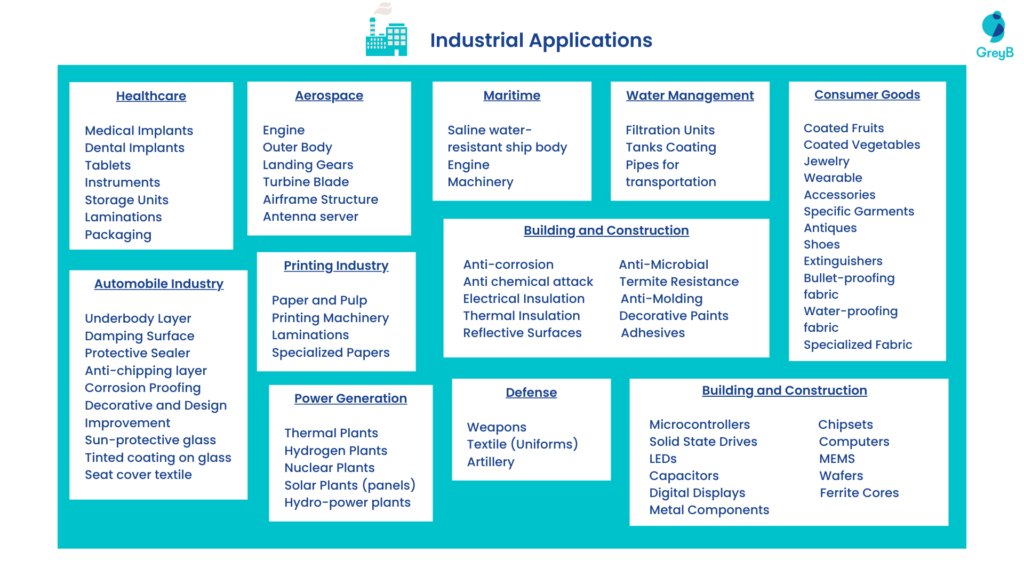
Which application areas have the largest market prospects?
Due to the huge number of applications of sustainable coatings, we have picked only a handful of major application areas for our analysis. Let us have a look at their current market size, expected growth, and future predictions of market size.
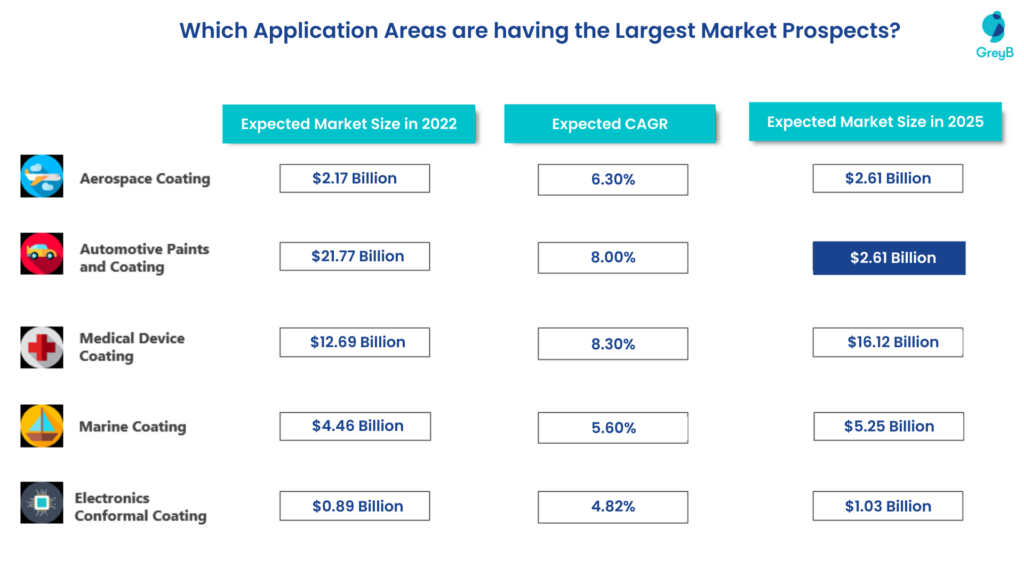
How has the innovation in major application areas been?
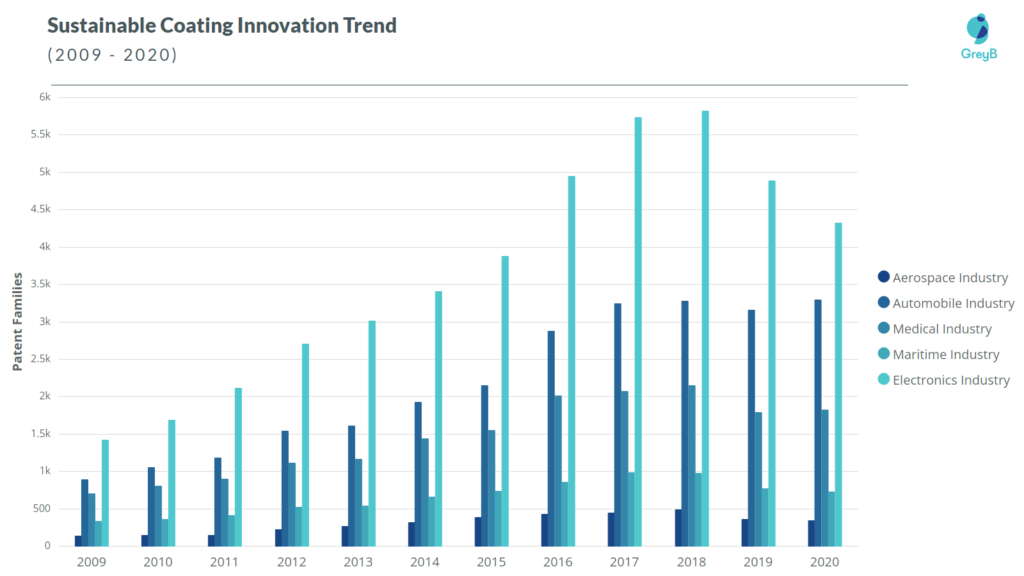
The above graph analyzes the Sustainable Coatings’ patents in the last 11 years aimed at the major application areas. Some patents have technologies that can have multiple applications too, therefore, we have counted them as a separate entity in each area as mentioned in their patent.
Key takeaways –
- Sustainable Coating innovation in the Automobile Industry grew at a CAGR of 11.51% from 2009 to 2020, the highest rate among these five application areas.
- The Electronics Industry has witnessed the highest volume of innovations (patent priorities) compared to the other four application areas in Sustainable Coatings. This can be attributed to the shift from the industrial age to the information age and the utility of semiconductors and microcontrollers in almost all walks of life.
Transport Industry (Road, aviation, rain, and shipping) was responsible for about 1/6th of the global greenhouse emissions in 2016. The net total that year was 49.4 billion tonnes of CO2 eq. (Source)
This is one of the prime reasons green coatings’ innovation in the Automobile, Maritime, and Aerospace industries is rapidly increasing. Moreover, automobiles today involve a lot of semiconductor chips and sensors that integrate certain digital functionalities. Similarly, the new-age medical devices and aerospace industry also demands more sustainable semiconductors and microcontrollers.
Research, development, and commercialization of sustainable electronic components will likely increase significantly in the future. However, the global chip shortage and international trade wars might alter the demand for green semiconductor coatings.
Competitive Landscape

Major Acquisitions and Collaborations
- PPG acquired Alpha Coating Technologies
PPG acquired Alpha Coating Technologies (a U.S.-based powder coating manufacturer) in March 2020 to expand its powder coating facility. This acquisition provides additional powder capacity, including small batch and low-cure powder manufacturing capabilities for general finishes, light industrial, furniture, and heat-sensitive substrate end uses. It also provides emerging IP in ultra-low-temperature cure powder technology.
With this acquisition, PPG will enter the growing market for powder on heat-sensitive substrates, such as medium-density fiberboard (MDF), high-density fiberboard (HDF), and hardwoods. (Source)
Powder coatings may require up to 500°F for proper application. Low-temperature cure powder technology supplemented PPG’s ongoing research into low-temperature powder coating manufacturing.
As a result, in November 2020, PPG introduced ENVIROCRON™ HeatSense powder coating for heat-sensitive wood and wood-composite applications, such as medium-density fiberboard (MDF), hardwood, plywood, and similar products. The coating can cure in as few as five minutes at 250 degrees Fahrenheit, be applied uniformly over heat-sensitive substrates, and accommodate the shrinking and swelling of wood over the finished product’s lifetime. (Source)
However, Akzo Nobel’s Interpon W (powder coating solutions for heat-sensitive wood and plastic) is still leading the race of ultra-low temperature curing by getting cured at as low as 80°C-120°C (170°-250° F). (Source)
- Hempel acquired Wattyl
A leading coating manufacturer, Hempel acquired major coatings manufacturer Wattyl Australia and New Zealand from The Sherwin-Williams Company (the world’s largest paint and coatings company) in 2021. Hempel is undertaking Wattyl’s for the decorative and protective coating segment with a turnover of €150 million and 750 employees.
With Wattyl as part of their company, Hempel is seeking to gain a strong footprint in Australia and New Zealand while pursuing its strategic ambitions for the Decorative, Infrastructure, and Energy segments in the South & East Asia region (Source)
Wattyl’s acquisition would help Hempel become a leading protective and decorative coating company. Furthermore, Hempel has expanded in selected geographies and jurisdictions for the past few years. This aligns with Hempel’s ambition of doubling its revenue to EUR 3 billion by 2025, as outlined in its Double Impact strategy. (Source)
- Koehler collaborated with Darmstadt Technical University
Koehler and Darmstadt Technical University collaborated and founded a laboratory, “Green Coating Collaboration.” The collaboration focuses on barrier coatings that can give flexible packaging paper properties that previously only plastic could offer. These include mineral oil barriers, water vapor barriers or barriers for oils and fats, and aroma barriers.
Their main goal is to find and test more sustainable, bio-based raw materials for barrier coating to use them on the production line ultimately. (Source)
- Brock University collaborated with Vanchem Performance Chemicals
Sheets made out of steel or other metals must be ‘pre-treated’ with a substance that will guard them against damage caused by rust and salt. This substance must stick not only to the metal but also to any paint applied to the sheets on top of the coating. Traditional coating systems used heavy metals – such as zinc and iron phosphates. Phosphates released into the environment cause algal blooms in lakes and rivers, damaging aquatic plant and animal life.
To overcome this problem, Paul Zelisko (a chemist from Brock University in Canada), along with Vanchem Performance Chemicals, has created (and patented US20170009083A1) a technology “Greencoat”, which uses silicon rather than heavy metals to bind coatings to both metal surfaces and paint. It’s a water-based system that has reactive sand in it. (Source)
- IFS Coating to use TerraPass Carbon Offsets
A privately owned manufacturer of sustainable powder coatings, IFS Coatings, would purchase monthly carbon offsets to further its work toward becoming more sustainable. IFS uses terrTerraPassgram to offset its carbon footprint, as claimed in 2021.
The TerraPass system invests in carbon reduction projects, and carbon offsets purchased through TerraPass support a diversified portfolio of projects in communities around the US and the world, including reforestation, renewable energy produced by wind power, and methane capture at dairy farms, landfills, and abandoned coal mines. All TerraPass projects meet the highest quality, monitoring, and independent verification standards. (Source)
Replacing all metal-based solvent-borne coatings with powder coatings could reduce the Green House Gas (GHG) equivalent to:
- The annual emissions of approximately 9.5 million cars, or
- Approximately 2.9 million trips around the world in a car
This could push IFS’ rank upward in the Top 25 Coating Companies list.
What type of innovation are the major universities focusing on?
Rice University edible and washable protein-based coating
Led by a Bangladeshi scientist, a group of researchers at Rice University in Texas developed a way to enhance the shelf life of fruits and vegetables using an entirely edible and washable protein-based coating.
The mixture of coating, mixed egg white, yolk, cellulose from wood, and a turmeric extract called curcumin keeps the perishable goods fresh for days.
According to the researchers, egg-based coating significantly reduces oxygen exposure and water loss. The coating retained freshness, appearance, and aroma for at least one week longer than the uncoated samples. Additionally, the researchers will work to test a spray protein to make it easier for both commercial providers and consumers looking for an at-home option. (Source)

Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering HydroFichi Project
Currently, different types of toxic and petroleum-based substances, like perfluorinated chemicals, are used to make a textile water repellant that harms the environment. To solve this problem, the Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology (IGB) has been researching sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives.
At the end of January 2021, they completed the HydroFichi (Hydrophobic Finishing with Chitosan) project. The result is a technology that can be used to give fibers desired properties using biotechnological processes and chitosan. (Source)
Notable Startups in the Sustainable Coating Industry
1. Auro
Headquartered in Germany, Auro USA sells bio-based paints, natural oils, and waxes. Their paint compositions consist of renewable natural materials and minerals, free of VOCs & formaldehyde. They have also created a unique biogenic binding agent, Replebin®, which grants high abrasion resistance, reduces drip or spatter, has zero emissions, and is safe to use in living areas.
Auro USA’s paints are available in various colors, finishes, and applications. They also offer a variety of natural oils and waxes for wood finishing.
Moreover, Stiftung Warentest, a German consumer organization, has declared AURO Woodstain No. 160 as the test winner (05/2006, test on wood stains). (Source)
2. Cypris Materials
Cypris Materials is pioneering a revolutionary approach to sustainable color production, expanding the color spectrum while streamlining manufacturing and application processes. The startup focused on developing sustainable structural color coatings. Their innovative technology aims to eliminate the need for toxic pigments in various industries. (Source)
Their innovative structural coating platform, supported by a robust patent portfolio, enables industry leaders to achieve unique colors and effects previously unattainable with conventional methods. Cypris’ proprietary polymers form the foundation of this groundbreaking technology. This is achieved through precisely engineered polymer layers that manipulate light to produce specific colors. The polymers self-assemble into a photonic crystal structure, selectively reflecting certain light wavelengths, resulting in pure, vivid colors.
By offering this innovative solution, Cypris Materials is poised to transform various industries. It will provide vibrant, durable, and eco-friendly color options while simplifying formulation and application processes.
The benefits of Cypris Materials’ technology include improved sustainability, as its copolymer is made from 50% plant-based raw materials that are both renewable and sequester carbon as they grow. (Source)
3. Relement
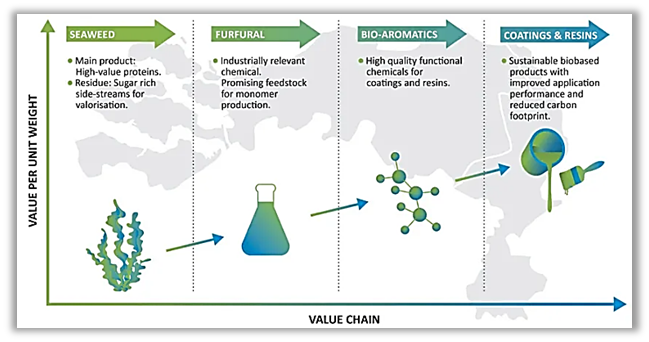
Relement, founded in 2020 (along with other partners like TNO, Green Chemistry Campus, Avans Hogeschool, Maastricht University, and Engineering Chemicals), is researching developing a biobased coating using seaweed. Seaweed produces high-value proteins, a by-product of which is non-edible sugar streams. Relement uses this by-product to create 100% biobased alkyd resin coatings that are more durable, cost-effective, and sustainable.
The institutes such as TNO, Avans, and Maastricht University have knowledge and technology in the fields of biorefining, bio-aromatics production, coating resins, and sustainability analyses.
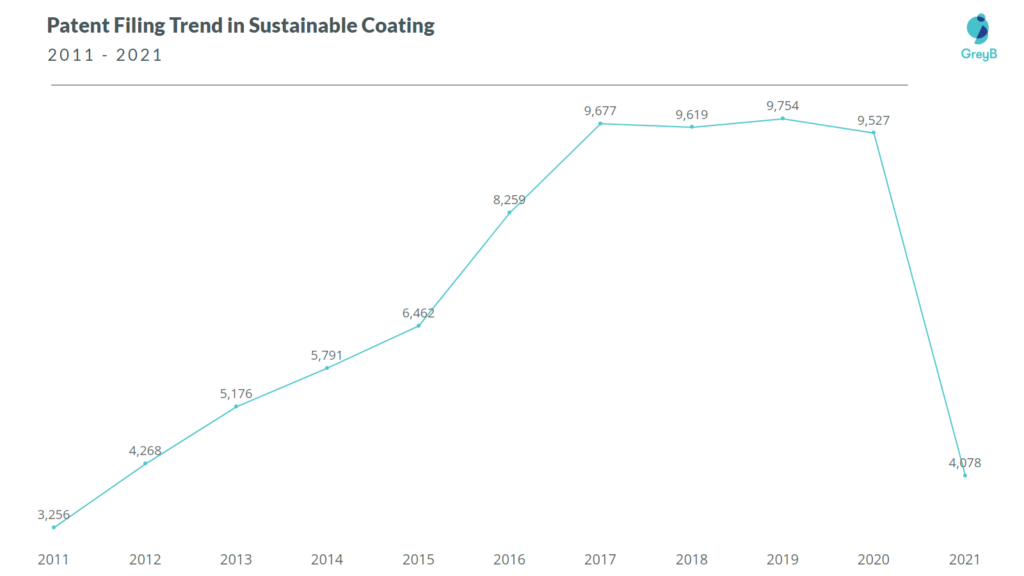
Patent Filing Trend in Sustainable Coating
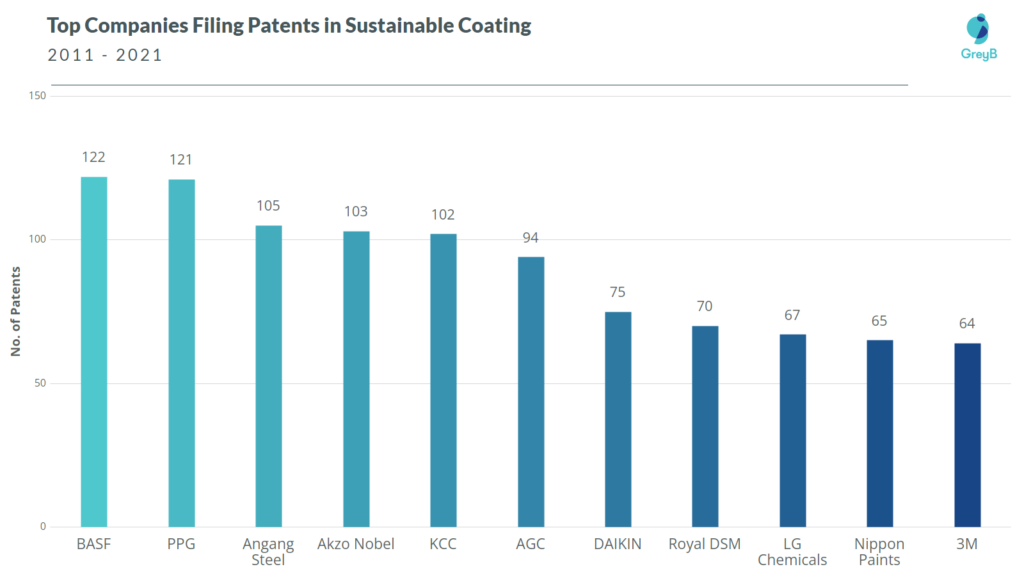
Chemical Companies are leading the patent filing in sustainable coating, as shown in the chart below:
Key Takeaways from Patent Filing Trend:
- BASF, Akzo Nobel, and PPG Industries are some of the major players in the sustainable coating industry and the antimicrobial coating, antifouling paints and coatings, and Hull Coating market. (Source, Source, Source)
- The top 11 companies are from diversified geographies such as the United States, Europe, and East Asia. However, four (AGC, Daikin, LG Chemicals, and Nippon Paints) of them are from Japan. This points toward the monopoly of the Japanese chemical and coating industry.
- Akzo Nobel (in 2017) claimed to have opened the world’s most sustainable paint factory powered by biomass and solar fuel. This factory recycles the residue water and solvents and, thus, develops a circular economy for waste management and resource optimization. (Source)
- Patent filings will increase at an average rate of 13% annually until 2020. This increase is attributed to increasing climate awareness and major companies’ visions to reinvent their coatings and paints in a sustainable form.
Have the central governments taken any initiative to promote sustainable coating?
The US and China are not just the world’s first and second-largest economies but also the second and first-largest carbon emitters. To support their net-zero targets, they are already taking a lot of initiatives to reduce emissions in major industries like coatings.
United States
- In December 2018, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed new greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) regulations to modify and reconstruct power plants. This rule would replace EPAs 2015 carbon pollution standard for new power plants. Such regulations promise environmental sustainability and push the demand for bio-based epoxy resins, thus raising the market’s growth rate. (Source)
- The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposes to amend the National Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Emission Standards for Aerosol Coatings. In this action, the EPA is proposing to update coating category product-weighted reactivity limits for aerosol coatings categories; add new compounds and reactivity factors (RFs); update existing reactivity values; revise the default RF; amend the thresholds for compounds regulated by this document, and add electronic reporting provisions. (Source)
China
- In 2016, China issued a consumption tax on coatings, effectively removing water-based coatings from taxation provided production was below the VOC emission taxation threshold. (Source)
- China removed water-based coating waste from the inventory of hazardous wastes, hugely reducing regulatory compliance requirements for the manufacture, import, and sale of these products. (Source)
- In 2017, the Shanghai Housing and Urban Development Management Commission announced a prohibition on using solvent-based coatings for exterior walls and wood-ware in construction. It went into effect on 1 May 2018. (Source)
- In Shanghai, after 2017, a tax of RMB 20 was levied on every kg VOC discharged. (Source)
Japan and India (the third and fourth highest emitters) are also expected to release similar policies in the future. Thus, sustainable coatings are a promising space for existing companies and newer startups to enter. Multiple M&A opportunities might also be created in the upcoming years.
Conclusion
Industries have come to understand the importance of sustainability and are moving towards a sustainable future. The coating industry is also following the lead and innovating. As a result, it has constantly been rising over the past few years. Startups and Universities are stepping in and collaborating with companies to deliver exceptional products.
So, if you are interested in coating research and want to have other crucial insights, fill out the form to share your problem with us:
Authored by: Sarvagya Saxena, Landscape Team.