Startup scouting identifies relevant startups to work with, usually in their early stages. This approach aims to create a radar that can assist organizations in quickly and successfully finding what they’re looking for.
Startup scouting is a vital expertise that can open a world of opportunity for organizations looking to innovate, invest, and expand. Companies that scout startups can access new sources of innovation while staying ahead of the technology curve by staying current with the latest developments.
Effective startup scouting can result in lucrative collaborations that drive innovation, promote growth, and provide a sustained competitive edge.
The innovation environment is changing as significant organizations grasp the value of startup scouting. Startups are essential in driving significant innovations that disrupt industries from hospitality to mobility and financial services.
Scouting and collaborating with startups allows organizations to explore and experiment with new technology and service solutions while lowering costs and risks to their core operations. Startups also provide a source of new talent and unique ideas, bringing energy to corporate cultures.
According to a KPMG survey, 88% of corporate participants deemed collaboration with startups critical to their innovation strategy. Open innovation is progressively being done through formal agreements with startups.
Working with startups to develop innovative ideas and products is often a faster and less risky option than internal development, as entrepreneurs bring fresh technology, business models, and expertise to the table.
According to an industry leader in technology scouting and open innovation, Alan G. Lafley, CEO of Procter & Gamble, states, “Half the company’s ideas must come from the outside”.
Technology and Startups Scouting aids in the identification of intellectual property and its commercialization through acquisitions, licenses, collaborations, contests, or crowdsourcing, among other things, to accelerate domestic innovation.
The process promotes open innovation by bringing the challenge of innovation to a broader technical community, which includes startups, SMEs, and universities. This improves the organization by speeding up the innovation process.
Download the Comprehensive Strategic Startup Scouting Guide for a detailed exploration of advanced scouting methodologies:
Overview of the Scouting Process
Startup scouting has evolved into an efficient way to achieve an organization’s innovation goals by developing new goods and services. As a result, startups can encourage innovation by accelerating product development, applying new technologies, and creating new business prospects. Some of the startup scouting process/ steps include:
Identify and Scope out the Need
Scouting is based on strategic growth, transformation, product innovation, and corporate management perspectives. As a result, it is critical to establish what is required to build a successful business innovation and explain why it is essential.
For startup scouting, brainstorm about industry trends and comprehend concrete future-related challenges. Breaking down the needs by product, market, company strategy, management team, and corporate innovation goals can assist in shaping the scope.
Align Stakeholders
Corporate innovation requires the involvement of both internal and external stakeholders. All stakeholders must be aligned and follow the defined strategy to meet particular milestones. Stakeholder alignment can be facilitated using various approaches, including one-on-one meetings, seminars, surveys, online platforms, and learning sessions.
Teams working toward a common innovation goal, such as the innovation management team, product management team, top management team, and others, have a standard strategy knowledge. This increases the possibility of accomplishing the intended outcome.
Maintain a Startup Scouting Stack
Scouting for innovative startups is a complex undertaking that cannot be completed with a single device or person.
Several factors must be introduced simultaneously to ensure the success of startup scouting. Consequently, creating a toolkit comprising a scouting platform, a team management facilitator, a database, and other such items is critical.
Maintain Clear Briefings
Writing a precise summary describing precisely what the corporate innovation specialist is looking for is critical. Developing corporate innovation necessitates a thorough awareness of the balance between clarity and openness in briefings. It is a challenging practice since startup scouting requires precise boundary drawing.
Allowing for serendipity increases the likelihood of discovering intriguing startups. There is a clear link between how one structures one’s thoughts while writing and expecting the result. Much external assistance helps develop the correct balance.
Assigning a Specific Team
Startup scouting is a very challenging activity that requires adequate resources to complete. The specialized task must be assigned to a specific internal employee. The individual must be educated about potential innovation milestones and overall industry trends and, most crucially, have enough time and attention to contribute.
Interact with the Startup Scout
Human relationships serve as the foundation for startup scouting. Communication among partners, scouts, internal employees, and external stakeholders will improve the scouting process. Sharing knowledge across multiple parties will bring complementary elements to technology.
A specialist with valuable skills in several innovation startup industries, such as healthcare, finance, sustainability, product development, etc., would assist the corporate process of seeking and identifying.
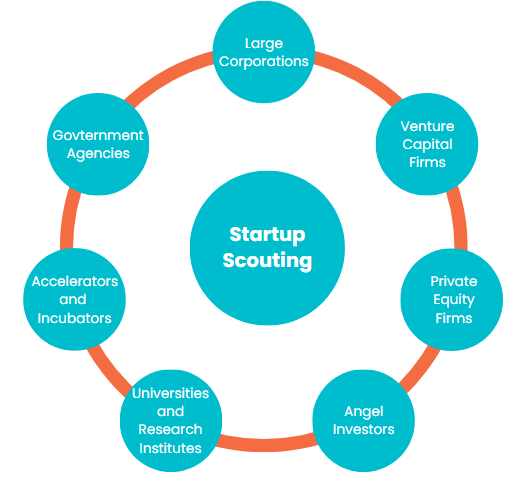
Need and Purpose of Startup Scouting
Large Corporations
Corporations need startup scouting for several strategic purposes, each contributing to their long-term success and competitive advantage:
- Discovering New Technologies and Innovations: Startups are frequently at the forefront of technological advancements, introducing new ideas and innovative products that can disrupt entire industries. By scouting startups, corporations gain early access to these emerging technologies, allowing them to integrate innovations into their operations. This approach helps corporations avoid technological disruptions and maintain a competitive edge in dynamically changing industries.
- Identifying Investment Opportunities: Corporations scout startups to identify promising investment opportunities. Startups represent a gateway to innovative technologies and business models that can offer substantial returns. By investing in startups, corporations can diversify their portfolios and reduce the risks associated with underperforming investments.
- Building Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with startups provides corporations unique opportunities to build strategic partnerships. These partnerships can enhance a corporation’s capabilities by leveraging startups’ agility and creativity, leading to product development and innovation breakthroughs. Such collaborations also open doors to co-investment and joint ventures, fostering long-term relationships that benefit both parties.
- Talent Acquisition: Startups are a valuable source of top-tier talent, particularly in cutting-edge fields. By scouting startups, corporations can identify and recruit skilled individuals who bring technical expertise and an entrepreneurial mindset.
- Tracking Industry Trends and Disruptions: Startups are often early indicators of emerging trends and potential industry disruptions. By monitoring their growth and direction, corporations can gain insights into the industry is direction. This information is critical for making educated strategic decisions, allowing corporations to adapt their business models proactively.
Venture Capital Firms
Venture capital firms rely on startup scouting to uncover opportunities that can shape their investment strategies and drive growth, such as:
- Identifying Investment Opportunities: Venture capital firms need startup scouting to discover high-potential startups that may not be on their radar. Scouts expand the firm’s deal flow by identifying unique and promising investment opportunities, ensuring that VC firms can act quickly to secure stakes in startups before their competitors do.
- Expanding Geographical Reach: Startup scouting helps VC firms access startups in regions and communities that might be overlooked. This geographical and demographic expansion allows firms to diversify their investments, reaching innovative companies across different markets and sectors, which could be pivotal for long-term growth.
- Tracking Industry Trends and Disruptions: Startup Scouting helps VC firms monitor their networks for startups making significant impacts in their industries, allowing VC firms to stay ahead of emerging trends and potential disruptions. This intelligence is crucial for making informed investment decisions and adapting strategies to remain competitive.
- Promoting Diversity: Scout programs are also instrumental in promoting diversity within the VC ecosystem. By integrating a broader range of individuals in the investment process, scout programs help VC firms access a more diverse set of startups, which can lead to more innovative and inclusive investment portfolios.
Private Equity Firms
Private equity firms leverage startup scouting to strategically position themselves for future growth and investment success, such as:
- Identifying Investment Opportunities: Startup scouting enables private equity firms to identify promising early-stage companies that can be developed into valuable assets. This early identification allows PE firms to secure investment opportunities with solid growth potential before these companies become widely recognized.
- Finding Potential Acquisition Targets: Scouting helps private equity firms uncover startups that align with their acquisition strategies. By identifying these companies early, PE firms can negotiate favorable terms and execute strategic acquisitions that enhance their portfolios.
- Tracking Industry Trends and Disruptions: Scouts provide private equity firms valuable insights into emerging industry trends and potential disruptions. This market intelligence helps PE firms decide where to allocate resources and which sectors to focus on for future investments.
- Talent Acquisition: Scouting isn’t limited to identifying companies; it also helps private equity firms discover and attract top talent. Startups often have highly skilled teams, and acquiring these companies can provide PE firms with the expertise needed to drive the success of portfolio companies.
Angel Investors
Angel investors rely on startup scouting to uncover promising opportunities and support innovation in the early stages of a company’s journey by:
- Identifying High-Potential Investments: Startup scouting allows angel investors to discover early-stage companies with significant growth potential. By identifying these startups early, angel investors can invest at lower valuations, increasing the potential for substantial returns as the company scales.
- Mitigating Risks: Scouting helps angel investors thoroughly evaluate startups, reducing the inherent risks of early-stage investing. Through careful analysis, they can better assess a startup’s viability and potential challenges before committing capital.
- Diversifying Portfolios: Angel investors use scouting to diversify their investments across various industries and sectors. This diversification helps spread risk and increases the likelihood of high returns from different ventures.
- Staying Competitive: In the highly competitive startup ecosystem, scouting enables angel investors to stay ahead by identifying promising startups before more prominent investors get involved. Early investments in such startups can yield significant advantages in future funding rounds.
Governments and Economic Development Agencies
Governments and Economic Development Agencies rely on startup scouting to drive regional and national growth through innovation, job creation, and strategic partnerships by:
- Fostering Regional Economic Development: Startup scouting helps governments and economic development agencies stimulate regional economies by supporting businesses that create jobs, innovate, and attract investment. This drives overall economic prosperity and improves the quality of life in their communities.
- Talent Acquisition: Startups are often rich in skilled and innovative talent. Governments can tap into this talent pool by supporting startups, helping to retain and attract highly qualified professionals to their regions, which is essential for future economic growth.
- Building Strategic Partnerships: By identifying them, governments can foster strategic partnerships between innovative startups and established businesses, academia, or public institutions. These collaborations can drive regional innovation ecosystems and support long-term economic development.
- Addressing Societal Challenges: Startups often offer unique solutions to pressing societal challenges, such as healthcare, sustainability, and digital transformation. Governments can leverage these innovations to improve public services and address issues critical to their citizens.
Accelerators and Incubators
Accelerators and Incubators require startup scouting to review thousands of early-stage startups and identify the top prospects for funding and mentoring through their rapid growth programs by:
- Identifying High-Potential Startups and Investments: Scouting allows accelerators and incubators to discover early-stage companies with strong growth potential. By identifying startups with innovative ideas, they can invest resources in ventures more likely to succeed, ensuring a solid pipeline for their programs.
- Diversifying Portfolio: A wide-ranging scouting process enables accelerator and incubator programs to build a diverse portfolio of startups across various industries and sectors. This diversity helps mitigate risks and increases the chances of producing successful outcomes from their cohorts.
- Networking and Strategic Partnerships: Startup scouting often involves connecting with various stakeholders, including investors, industry experts, and other entrepreneurs. These connections help accelerators and incubators expand their networks, which can be valuable for the startups they support and their long-term success.
- Fostering Innovation: Accelerators and incubators are hubs of innovation. Scouting helps them stay competitive by identifying startups pushing boundaries and driving technological advancements. This, in turn, fosters a culture of continuous innovation within their programs.
Universities and Research Institutions
Universities and research institutions scout startups working on cutting-edge research with commercial potential for collaboration opportunities for:
- Discovering New Technologies and Innovations: By actively scouting startups, universities can tap into diverse new technologies and ideas outside their research domains. This approach allows universities to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, improving their capacity to develop novel solutions and remain competitive in research.
- Fostering Regional Economic Development: Universities contribute to regional economic development by supporting startups through startup scouting. Successful startups can create jobs, stimulate local economies, and enhance the university’s reputation as a hub of innovation.
- Talent Development and Acquisition: Universities can use startup scouting to identify opportunities for students and researchers to gain practical experience, entrepreneurial skills, and industry exposure. Collaborations with startups can also lead to talent acquisition, with universities attracting skilled professionals from the startup ecosystem to join their academic and research teams.
- Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Startups offer innovative approaches and flexibility that complement academic research. Universities and research institutions can partner with startups to enhance their research capabilities and foster innovation.
Evaluation Criteria of Startup Scouting
Team and Leadership
Facebook Acquired FriendFeed to Enhance Engineering and Product’s Team and Leadership
- In 2009, Facebook acquired FriendFeed, an innovative online sharing service. The acquisition’s financial terms were not disclosed, but the deal included integrating FriendFeed’s team into Facebook’s engineering and product departments.
- A central element of the acquisition was integrating FriendFeed’s talented team and its four co-founders, who brought significant expertise from their previous roles at Google. Bret Taylor, co-founder and former Google Maps group product manager, and Paul Buchheit, known for Gmail, joined Facebook.
- The addition of FriendFeed’s team was leveraged to enrich Facebook’s creative and technical resources. Their leadership and experience were expected to drive innovation and enhance Facebook’s product development capabilities.
Microsoft Acquired GitHub to Enhance Developer Collaboration and Talent Acquisition
- In 2018, Microsoft acquired GitHub, a code repository service, for $7.5 billion. This strategic move allowed Microsoft to tap into the rich talent pool within GitHub and strengthen its commitment to open-source development.
- A significant aspect of the acquisition was talent acquisition. GitHub’s experienced team of developers and leaders joined Microsoft. This acquisition enabled Microsoft to scale its participation in open-source projects from 2,000 to 25,000 engineers, expanding its influence and contributions to projects such as TypeScript, .NET, and Windows Terminal.
Market Potential and Size
Google Acquired Fitbit to Expand into Wearable Tech
- In 2021, Google strategically acquired Fitbit for $2.1 billion to strengthen its position in the wearable technology market and enhance its health and fitness data capabilities.
- The move enabled Google to compete more effectively with companies, including Apple and Samsung, in the wearable tech space. Google did not have a direct competitor to the Apple Watch, and this acquisition provided an opportunity to enter the fitness device market. However, the acquisition faced regulatory scrutiny due to concerns about privacy and the potential integration of Fitbit’s supply chain with Google’s existing operations.
- This acquisition marked Google’s significant entry into the wearable technology sector. Merging Fitbit’s expertise with Google’s resources addressed essential privacy issues and advanced health data analytics.
Microsoft Acquired Activision Blizzard to Expand in the Gaming Industry
- In 2022, Microsoft announced its acquisition of Activision Blizzard to expand its market share in the gaming industry and capitalize on Activision’s renowned franchises, such as Call of Duty. The deal, valued at approximately $69 billion, set a record as one of the largest in the industry. Microsoft saw it as a strategic acquisition given its growing influence in the cloud gaming sector, where games are designed to be compatible across various platforms and enable inter-console gaming.
- The acquisition faced regulatory scrutiny due to concerns over market consolidation and internal issues within Activision. Microsoft addressed these concerns during the due diligence process and effectively navigated the integration of the two companies.
- This acquisition significantly bolstered Microsoft’s gaming portfolio, accelerated the growth of its Game Pass service, and enhanced its presence in the emerging metaverse space.
Product or Technology Innovation
Keery Acquired Natreon to Drive Innovation in Functional Food
- In 2022, Kerry completed the acquisition of Natreon to expand its ProActive Health portfolio of science-backed branded ingredients. This acquisition supported Kerry’s technological growth and allowed Natreon’s ingredients to be integrated into Kerry’s global application and R&D network.
- Kerry plans to leverage these ingredients, protected by numerous U.S. and foreign patents and supported by 52 clinical studies, to enhance its offerings and continue investing in the science and clinical evidence behind the brands. By incorporating proven Ayurvedic botanicals, Kerry will strengthen its health and wellness market position.
Cisco Acquired Lightspin to Enhance its Existing Offerings
- In 2023, Cisco acquired Lightspin Technologies, a company specializing in cloud security posture management (CSPM) for cloud-native resources.
- Lightspin uses graph-based technology to provide context, prioritization, and remediation recommendations, allowing customers to identify and mitigate cloud security risks with minimal configuration.
- The acquisition enabled Cisco to develop Panoptica, a cloud-native application platform that offers features such as attack-path analysis, cloud detection and response, application security, code vulnerability detection, and cloud security posture management. This strategic move enhances Cisco’s ability to provide comprehensive cloud security solutions across its customer base.
- Cisco planned to integrate Lightspin Technologies into its Emerging Technologies & Incubation (ET&I) business unit. This group is responsible for exploring new product ideas and innovations in various segments, including the cybersecurity market.
Business Model and Scalability
Lendingkart Acquired Upwards Fintech to Strengthening its Presence
- Lendingkart’s acquisition of the digital lending platform Upwards in 2023 gave Upwards access to Lendingkart’s credit, capital, and distribution network, enabling it to expand its presence across India.
- This acquisition also strengthened Lendingkart’s offerings, particularly those aimed at small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), by incorporating Upwards’ advanced technology stack. Additionally, Lendingkart deployed Upwards’ credit underwriting engine to enhance the user experience and streamline the loan disbursement process, further improving efficiency in its lending operations.
Siply Acquired myPaisaa to Enhance its Existing Offerings
- In 2023, Siply acquired the chit fund app myPaisaa for $7.5 million to expand its digital financial services.
- This acquisition enhanced Siply’s offerings by integrating myPaisaa’s chit-fund distribution platform, broadening its customer base.
- The strategic move aligns with Siply’s mission to provide innovative, fully digital, sachet financial services, ultimately driving growth and promoting financial inclusion across India.
Competitive Advantage
Salesforce Acquired Slack to Gain Competitive Advantage over Microsoft Teams
- In 2021, Salesforce acquired Slack for $27.7 billion. This strategic move bolstered Salesforce’s position in the enterprise communication market and directly competed with Microsoft Teams.
- By acquiring Slack, Salesforce aimed to create a stronger counterforce against Microsoft Teams. Integrating Slack with Salesforce’s Customer 360 platform was intended to offer a compelling competitive advantage to Microsoft’s communication and collaboration tools, enhancing Salesforce’s market position in enterprise software.
Traction and Growth Metrics
Spotify Acquired Anchor to Boost Podcast Growth
- ·In 2019, Spotify acquired Anchor, a startup specializing in podcast creation, publishing, and monetization, for over $100 million. This strategic move expanded Spotify’s podcast capabilities.
- Following the acquisition, Anchor-powered podcasts surged, representing 80% of new podcasts on Spotify by 2020. This significantly contributed to Spotify’s overall growth, boosting user engagement and retention.
- Anchor’s integration also resulted in higher “time spent listening” metrics on Spotify compared to other podcast hosting providers, solidifying Spotify’s traction in the competitive streaming market.
Uber Acquired Postmates to Boost Delivery Growth
- In 2020, Uber acquired Postmates, a food delivery service, for $2.65 billion. The acquisition was part of Uber’s strategy to diversify its offerings and strengthen Uber Eats during the pandemic.
- After its acquisition, Uber Eats saw a significant boost in market growth, especially in critical regions such as Los Angeles and the American Southwest. The expanded network of restaurants and variety of goods facilitated through Postmates allowed Uber Eats to penetrate the market further and attract new customers.
- Integrating Postmates’ established partnerships and delivery infrastructure enhanced Uber Eats’ market reach and operational efficiency, contributing to more substantial traction in the competitive food delivery sector.
Financials and Funding History
Visa Acquired Currencycloud to Boost its Foreign Exchange Capabilities
- Visa acquired cross-border payments firm Currencycloud in 2021 in a £700 million deal. This acquisition aims to strengthen Visa’s foreign exchange capabilities by expanding its services to support financial institutions, FinTechs, and partners.
- Currencycloud, known for processing over $5 billion in cross-border transactions monthly, had a strong 2021, growing its team to nearly 500 employees.
- Visa noted that this deal would accelerate time-to-market and enhance payment transparency for clients seeking to offer more flexible, digital-first payment services, ultimately improving the efficiency and reach of Visa’s global payment solutions.
Alignment with Government Regulation
Microsoft Acquired BlueTalon to Strengthen Data Privacy and Governance
- In 2019, Microsoft acquired BlueTalon, a data privacy and governance service. This acquisition aimed to enhance Microsoft’s compliance capabilities and strengthen its Azure platform’s alignment with data protection regulations. BlueTalon’s data access management and governance expertise provided Microsoft with critical tools to support compliance with global data privacy laws such as GDPR and HIPAA. The acquisition enabled Microsoft to navigate complex regulatory environments.
Intellectual Property
L&T Semiconductor Technologies Acquired SiliConch Systems Pvt. to Enhance its IP
- In 2024, L&T Semiconductor Technologies announced its decision to require SiliConch Systems Pvt., an IC design startup, to strengthen its intellectual property and engineering capabilities in the semiconductor sector.
- This acquisition is part of a broader strategy involving investments in and acquisitions of India-based chip startups. SiliConch Systems’ IPs are primarily utilized by Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and fabless IC companies in the U.S., focusing on power management systems for smartphones, automotive applications, and accessories.
- This acquisition will significantly enhance Larsen & Toubro’s semiconductor business by integrating SiliConch’s intellectual property, engineering expertise, and design capabilities into its operations.
Tate & Lyle Acquired Most of Nutriati’s Assets
- In 2022, Tate & Lyle acquired most of its assets from Nutriati, a Virginia-based ingredient technology company known for developing chickpea protein and flour, for an undisclosed amount. The acquisition includes Nutriati’s intellectual property and selected liabilities.
- Nutriati has developed a patented process to produce functional chickpea proteins and flours, marketed under the Artesa brand. This acquisition strengthens Tate & Lyle’s position in the growing market for plant-based proteins, particularly chickpea-based ingredients. Additionally, several key members of the Nutriati team have joined Tate & Lyle, enhancing their existing engineering and formulation expertise.
Startup Scouting Process
Defining Objectives and Criteria
The startup scouting process begins with a company determining its unmet business needs and expected outcomes. Based on these needs, criteria are established to define the solutions demanded. These criteria include company type, age, location, funding stage, and technology. A vital part of this process is the role of innovation scouts, who are tasked with finding suitable startups and scaleups that meet these criteria. The scouting team, led by these scouts, conducts a topic-scoping process to assess the number of suitable solutions available. This process is relatively quick, providing an overview that helps decide whether to proceed with the topic or explore other options.
Determining investment or collaboration criteria is also crucial. To establish these criteria, the following factors must be considered:
- Investment or collaboration goals
- Industries or sectors of interest
- Targeted startup stage (early-stage, growth-stage, etc.)
- Geographic regions to be focused on
Addressing these questions makes the scouting process more focused and efficient, aligning with strategic objectives and increasing the likelihood of successful investments or collaborations.
During this stage, public web data can be utilized to analyze the targeted companies’ industry and business environment. This approach ensures that companies comprehensively understand potential solutions and their viability, supporting informed decision-making throughout the scouting process.
Identifying Sources and Channels
In the modern landscape, discovering promising startups has evolved beyond traditional methods such as networking. While conventional approaches remain viable, today’s startup search can be automated and enhanced through unconventional channels and sources. Instead of physically attending events to find new startups, automated solutions can now scan event websites to collect public information about participating startups. Public web datasets play a crucial role in this automated search process. These datasets help identify companies or industries showing early growth signs, pinpoint startups in urgent need of investment, spot startups nearing a mature stage, and find early-stage companies and technologies.
Additionally, technology-based startup scouting offers investors a competitive edge. It enables the screening emerging companies and technologies, gaining significant user attention. The key advantages of this approach include accelerating the process and aiding investors in uncovering hidden gems that might otherwise remain undiscovered. This technological approach speeds up the search and enhances the accuracy and depth of the scouting process, offering investors a competitive edge in identifying high-potential startups.
One should leverage multiple channels to identify promising startups, including pitch events, incubators, accelerators, startup databases, startup scouting platforms, startup scouting agencies, and personal networks. This approach broadens the search and enhances the likelihood of discovering startups that align with specific criteria, ensuring no potential high-value opportunities are overlooked. At this stage, scouts compile a comprehensive list of startups based on company criteria, but the initial search is broad, potentially resulting in thousands of relevant solutions.
Screening and Initial Evaluation
Screening evaluates scouted vendors to select the best options for a client’s needs. This step thoroughly examines the vendor’s product, solutions, customer support, and long-term vision. The Screening phase often requires internal review by the Scouting as a Service team and other stakeholders to ensure that when a vendor is presented to the client, it is done with a client-centric approach. This presentation includes relevant product information and emphasizes the positive impact and benefits for the client. The goal is to showcase vendors in the best possible light, aligning their offerings with the client’s specific requirements.
With numerous options available, the next step is to cluster and prioritize them. When a scouting platform identifies over 10,000 technology startups, trained Innovation Researchers and Analysts use Big Data, AI, and human expertise to refine these results. They ensure that the selected startups align with specific requirements and rank them according to set priorities. This process pre-selects the top solutions that address business challenges and ensures high relevance. The emerging companies are clustered into innovation groups, technologies, and application areas, providing actionable innovation intelligence. This approach empowers data-driven decision-making to advance corporate innovation strategies.
Due Diligence and Deep Dives
Deep diving into the competitive landscape provides valuable inspiration and insights regarding the partnerships that best support achieving goals. In the context of helping an entrepreneur raise money, deep-dive meetings with potential investors are inevitable. Whether dealing with the company’s initial investors or building a syndicate for a funding round, a successful pitch typically requests more involved meetings. These “deep dive meetings” sessions allow investors to unpack the company’s story in greater detail.
Due diligence is essential before engaging with startups. It thoroughly evaluates their viability by assessing business models, market potential, technology readiness, team capabilities, intellectual property, and financial health. Engaging relevant stakeholders within the corporation ensures diverse perspectives and a comprehensive assessment.
Technical due diligence validates a startup’s technology assets, risks, and liabilities. It aims to evaluate a product or service’s systems and infrastructure for possible risks, weaknesses, or gaps. This evaluation ensures that any issues that could hamper a company’s growth or compromise its ability to deliver on commitments to investors, customers, and partners are identified early. Investors perform technical due diligence in their overall assessment, including legal, financial, and other related activities.
Investors play a crucial and integral role in the due diligence process. They seek to comprehend and verify an investment opportunity’s technology assets, risks, and liabilities. Their assessments determine whether the technology assets are as described, the scope and scale of any associated risks, and which risks might present as current or future liabilities. This integral role makes them feel valued and essential to the process.
Interview or Talk to the Team/Founder
Once the deep-dive analysis is completed, the company evaluation and validation phase begins, involving interviews with founders or commercial teams. Every startup that has been sourced and channeled must be interviewed.
Two next-step options are recommended to facilitate necessary interactions: requesting a solution demo or negotiating for a freemium trial. It is also suggested that recommendations be sought from other venture capitalists (VCs) or clients. In the context of a venture client scouting model, profiles such as Head of Commercial, Business Development, and C-Level executives are ranked, which can help evaluate the viability of potential synergies.
Connecting with commercial teams is prioritized because they are always looking to develop new initiatives and establish potential partnerships, which helps expedite the process. If no commercial personnel are available, C-level executives may be contacted. In such cases, it is recommended to start by engaging with the CEO, followed by the CTO or COO. When reaching out to the business development manager, conveying a concise and accurate message is essential to initiate communication between both parties. Once contact is established, asking strategic and targeted questions on specific topics is recommended to gather additional information about the startup that may not be readily available.
GreyB’s Scouted is a scouting campaign where they interview startups.
Company Benchmark
After identifying the most innovative startups, the next step is to benchmark the comparative fit of these startups with the corporate needs identified in the startup scouting process. The corporate innovation team should review the shortlisted innovative startups seeking such innovations. Understanding the startup ecosystem enables clients to benchmark their offerings against those of innovative startups. This knowledge can improve their products or services, enhancing their competitive position in the market. It is recommended to start with a shortlist of market-leading startups and benchmark each one based on multiple parameters such as their business model, team, traction, and the uniqueness of their technology. By evaluating these factors, corporations can better understand how these startups align with their strategic goals and identify opportunities for collaboration or adoption of innovative solutions.
Reporting and Recommendation
Reporting is essential for making quality decisions, a fundamental aspect of scouting. This stage is vital in synthesizing findings and making actionable recommendations. It involves compiling comprehensive reports detailing the evaluation of startups’ startups, including their strengths, weaknesses, market potential, and alignment with the strategic goals. The report typically includes a summary of the due diligence performed, an assessment of the startup’s technology and business model, and insights into the competitive landscape.
Information scattered across numerous documents and sharing sites makes capturing all information and creating accurate reports difficult. Quality data is crucial for making proper decisions. Leveraging a single enterprise system to self-manage the process can simplify reporting.
The scouting team formulates recommendations based on the gathered data, identifying the most promising startups that best meet the clients. These recommendations are presented in a structured format, often accompanied by strategic advice on engagement and partnership opportunities. The goal is to provide the client with clear, actionable intelligence to make informed decisions on potential investments or collaborations.
Follow-Up and Relationship-Building
Following up is a crucial step in the call for projects process. The follow-up stage in the startup scouting process is vital for maintaining engagement and ensuring a thorough evaluation of potential startups. This stage begins immediately after initial contact and continues throughout the scouting process.
Promptly answering a startup’s questions and providing additional information as needed ensures clarity and demonstrates ongoing interest in the startup’s proposal. Proactive follow-up is essential to maintain the startup’s engagement throughout the process. Additionally, semi-annually, interviews are conducted with business units and group companies to collect and update on their innovation needs.
Strategies for Scouting Promising Startups
Online Platforms and Databases
One of the simplest methods to discover new startups is to visit online platforms featuring them. These sites might be generic, such as Product Hunt, AngelList, or Crunchbase, or industry-specific, such as MedCity News, Fintech News, or EdSurge.
These platforms allow users to search for companies based on categories, stages, locations, funding, and other criteria. Databases and dashboards are examples of technologies that provide data, insights, and recommendations about startups’ performance, traction, and potential. These platforms allow users to obtain market intelligence, industry trends, competition analysis, and value measures.
Example: StartUs Insights’ Discovery Platform is a powerful and easy-to-use tool for discovering the startup ecosystem. It allows users to filter out unnecessary companies from many results and identify the most exciting startup profiles to scout and work with.
Social Media and Professional Networks
One strategy for uncovering new startups is to follow social media outlets that discuss them. Social media may be an excellent resource for finding businesses to collaborate with and invest in. These platforms can include blogs, podcasts, newsletters, or video series highlighting startup-related interviews, insights, and trends. Some examples are TechCrunch, The Startup Chat, Y Combinator, and SaaStr.
These channels allow users to learn about founders, mentors, and investors’ tales, problems, and accomplishments. The user can also participate in the community and professional networking with possible leads. The user should also keep track of the startup’s founders’ participation in blogs, podcasts, and video series for thought leadership and industry insights.
Assessing the founder’s communication style, messaging consistency, and community involvement is also essential in categorizing the startups. Strong leadership is defined by high engagement, favorable feedback, and a proven track record.
Following relevant hashtags on social media is one approach to uncovering startup opportunities. The user should also connect with the startup’s founders and investors via social media. Example: Google+ features several beneficial communities for startup founders and investors. LinkedIn is an excellent medium for connecting with business founders and investors. The online platform allows users to search for persons with specific job titles, such as startup founders or CEOs.
Industry Events and Conferences
A third option for finding new startups is attending online events and conferences that link investors and startups. These events can include pitch competitions, demo days, webinars, or networking meetings highlighting the most recent developments and prospects in various industries.
Some examples of the events and conferences are Startup Grind, Techstars, 500 Startups, and GSV Ventures. These events let users view live or recorded pitches, ask questions, and schedule meetings with the founders. Several companies want to hear from successful founders about their journeys, the ups and downs, and what worked and failed. They also want to grow their networks and develop positive ties with other successful entrepreneurs.
They want to connect with influencers, ecosystem participants, and investors to understand the market and investment landscape. Most startup and tech conferences feature an app that allows users to communicate with other participants and people of interest to them. Startup conferences are attended by investors from all over the world who are looking for businesses to invest in. They allow entrepreneurs looking for funding to raise capital.
Accelerators and Incubators
A business accelerator and incubator aims to help entrepreneurs develop and thrive by providing various tools and services. These programs offer multiple incentives, including office space, mentoring, networking opportunities, and money. These incubators are frequently associated with government agencies or community organizations. Their mission is to promote economic development and encourage local enterprises. Some colleges include incubators that serve as a starting point for students to create and grow a startup or business.
These incubators also improve relationships between academic institutions and business players such as corporations and other startups, allowing them to gain valuable experience. Even large corporations operate corporate incubators to encourage internal innovation. Various entrepreneurs must submit their business ideas to requests for proposals within startup incubators and accelerators. Startup incubators include Climbspot, Cloud Incubator Hub, and InnovaUNAM, among others. The user should research various accelerators and incubators that provide a place for the required startups to grow, bloom, and innovate.
University Programs and Tech Transfer Offices
Universities’ functions in a startup ecosystem include talent pooling, knowledge transfer, incubators/accelerators, technology transfer and licensing, networking, and collaboration.
Universities serve as talent banks, boosting the talent pool for businesses. Another essential duty of universities is to convey information to entrepreneurs and the ecosystem via academic research, cutting-edge technology, and specialized skills. This transfer makes a substantial contribution to product creation and innovation. Universities provide networking opportunities through events, workshops, seminars, and conferences. These events allow startups to engage with potential partners, consumers, suppliers, and other stakeholders, thereby growing their network and opportunities.
The various universities’ programs provide a nurturing environment for startups to become actively involved in different industries. The programs invite students and the community to participate in consultations, project concept discussions, and workshops. Example: Research conducted at the University of St. Francis’s College of Business and Health Administration shows that the university has an incubator program that helps student companies and community entrepreneurs. Universities’ support for student businesses has been proven to improve their entrepreneurial skills.
Patent Databases
According to a new study, firms with patents and trademarks at their first seed or early growth phases are ten times more inclined to get funding. In recent years, the startup ecosystem has grown exponentially worldwide. In the complex environment of startup businesses, patents and trademarks emerge as critical competitive tools.
Users/investors must conduct patent searches in specific databases to identify their target startups based on product patents. Patent searches in any subject are time-consuming and complex. One must search through all accessible patent data using complicated Boolean queries, analyze it, and condense the fundamentals. The user can also utilize AI to search for certain patents and then analyze startups based on the results.
Local Entrepreneurship Ecosystems
Startup ecosystems are increasingly crucial to the modern economy, serving as hubs for entrepreneurs and investors. Building a thriving local startup ecosystem requires a strategic approach and an in-depth understanding of key factors influencing its growth and sustainability. These factors include funding availability and investment opportunities, a skilled and educated workforce, access to essential resources and infrastructure, and support from local organizations and government bodies.
Success in the startup world depends on creating a dynamic and supportive environment that promotes growth and creativity. Mapping the region is essential for understanding the local context and gaining a competitive edge. This approach also opens networking opportunities and enhances profitability for entrepreneurs.
By assessing essential resources such as education, internet access, and transportation, a productive startup ecosystem can be built to meet entrepreneurs’ specific needs, increasing their chances of success.
Referrals and Word-of-Mouth
Another option to uncover new companies is to join online forums with similar interests and ambitions through referrals or word of mouth. These communities can include forums, organizations, and referrals for investors, founders, and experts.
These groups and referrals allow users to ask questions, offer assistance, and receive feedback on their ideas and decisions. As the marketing world evolves, so does the importance of word-of-mouth marketing for discovering entrepreneurs. Word of mouth and referrals are one of the most cost-effective ways to identify and learn about numerous companies to be scouted.
Challenges in Startup Scouting
Information Overload and Noise
Startup scouting may be both thrilling and challenging. One of the most typical obstacles in this process is information overload and noise. Information on new startups and technologies is available from many sources and venues. As a result, it is difficult to separate the essential and trustworthy information for startups from the noise and distraction. The users use various tools and platforms to gather, categorize, and prioritize relevant startup information.
Assessing the Early-Stage Potential
One of the obstacles investors confront during the startup scouting process is determining the early-stage viability of startups. There is a shortage of historical data on numerous startups. Early-stage firms lack an operational history, making it incredibly difficult to assess the consistency and longevity of their influence.
Many companies have limited financial and human resources, affecting various operations elements.
As a result, investors face a challenge in accurately assessing the potential for long-term success and reliability in terms of impact. Early-stage businesses inherently include higher risks and uncertainties, making predicting the success of startups more difficult for investors.
Staying Ahead of Competitors
Through startup scouting, the firm can collaborate with startups and benefit from each other’s advantages. However, several obstacles, such as limited time and money, make it challenging to locate prominent startups and complexity in staying ahead of competitors in startup scouting.
While established firms could have more incredible resources and a recognizable brand, startups face challenges competing with a wide range of goods and services. Finding voids in their goods and services without speaking with rivals also becomes challenging because of limited networking.
Aligning Scouting with Organizational Goals
Startup scouting is vital, allowing the firm to identify, attract, and interact with innovative businesses that fit the organization’s long-term development objectives and goals. Aligning startup scouting with organizational goals can be challenging when objectives are unclear or communicated, resulting in a misalignment of scouting with the organization’s mission or vision.
Startups work in unpredictable situations, so matching scouting with long-term organizational objectives might be challenging when they are prevalent in an unstable market. Unexpected revocations or adjustments and natural or unnatural disasters may also make aligning scouting with organizational goals difficult. Startups need to coincide with both specific strategic and broader organizational goals. Sometimes, finding a balance between short-term demands and long-term goals can be difficult.
Dealing with Geographical Limitations
Limited resources and connectivity to local networks are some issues encountered during startup scouting, particularly when considering geographical limitations. Restricted budgets and human resources can hinder practical scouting activities. Substantial resources are in demand for scouting startups across different geographies. However, restricting geographical region segmentation can reduce the number of selected startups. One should prioritize locations depending on strategic objectives and the availability of resources when scouting for startups.
Even geographical barriers can prevent direct access to local startup ecosystems. Organizations should form alliances, attend global events, and establish ties with local accelerators or incubators to overcome these limitations.
Evaluating Technical Innovations
During the scouting startup phase, evaluating technical innovations may be complicated. Evaluating technical advancements demands extensive research into many sources and continual study, which can be resource-intensive for businesses and result in substantial time spent scouting.
Numerous news sources provide a wealth of information on emerging technology. Sorting through this technological information overflow to find significant advances might be difficult. During the launch phase, new technologies are evaluated based on risks such as security, compatibility with existing systems, and long-term viability.
Many firms struggle to identify promising technology. With the quick pace of innovation, businesses often struggle to keep ahead of trends and discover effective tech solutions that correspond with their strategic goals.
Navigating Cultural Differences
Even though startups are becoming increasingly popular, their culture has its own unique set of obstacles and challenges that are dedicated to being solved.
Cultural awareness is essential in startup scouting. The absence of it could cause a company to overlook regional obstacles, resulting in biased advice and misguided direction that could jeopardize its approach and the startup’s prospects.
Diverse cultural backgrounds lead to distinct viewpoints on firm processes, such as negotiation, time management, decision-making, and hierarchy. If not recognized and understood, these differences may cause conflict. Scouting activities may also become challenging because several countries/industries have separate legal and regulatory frameworks for individual startups. Understanding and managing these disparities is crucial for successful partnerships between startups.
Future Trends in Startup Scouting
Increased Use of AI and Machine Learning
Traditional startup scouting tactics, such as visiting events, networking, and comprehensive vetting, are frequently time-consuming, expensive, and geographically limited.
AI-powered Digital Startup Scouting represents an enormous leap forward in startup involvement, providing unprecedented efficiency, insight, and a vast potential for growth for corporate innovation projects in the future.
Integrating AI into the future scouting process will empower businesses to locate, appraise, and interact with startups with a newfound efficiency. AI-powered platforms provide essential insights about startup performance, market trends, and the competitive landscape, enabling more innovative, data-driven decisions and instilling confidence and control.
AI-powered digital solutions are easily scalable to meet expanding scouting demands and adapt to changing market conditions, providing firms with a dynamic and long-term innovation strategy. These AI technologies simplify communication duties and produce company ideas, streamlining the scouting process.
Cross-Border and Remote Scouting
Remote startup scouting is locating, analyzing, and engaging with early-stage startups via online tools and digital platforms without a physical presence. Various investors, large businesses, and venture capitalists have been using this process to identify new viable startups without requiring face-to-face meetings.
Remote startup scouting or cross-border scouting includes digital platforms and online networks, which the investors/Scouters use to identify new startups internationally. They also attend online pitch events and participate in digital communities while studying various scouting systems, which collect data from multiple sources to streamline the process.
Silicon Valley Innovation Center offers its customers remote startup scouting services. They create custom databases, communicate with qualified individuals online, and run pilot projects without needing in-person encounters. This technique has various advantages, including being cost-effective, time-efficient, and valuable for making data-driven decisions.
Sustainability and Impact
Previously, innovation scouting has been focused on technological developments and commercial disruptions. However, in recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors in the startup ecosystem. Scouts prioritize ESG innovation and look for firms committed to sustainable practices, ethical governance, and social responsibility.
Scouts support collaborations that use shared skills and resources to speed up the development and uptake of sustainable solutions. Scouts enable ecosystem-wide collaboration, resulting in synergies that multiply the effect of ESG-focused startups and accelerate systemic change.
Scouts evaluate startups’ resistance to environmental, regulatory, and reputational risks, ensuring sustainability is integrated into their growth strategy. By providing rigorous ESG frameworks to beginning companies, Scouts help establish resilient firms well-positioned for long-term success and beneficial societal impact.
Democratization of Access to Startup Information
Efforts are in progress to make scouting more accessible by expanding opportunities to a broader group of participants.
New platforms are being developed to link scouts with venture capital firms, increasing visibility and simplifying scouting. This push for democratization aims to make scouting an inclusive and accessible activity rather than one reserved for a select few.
However, it’s essential to be cautious. A potential downside of this democratization is the risk of producing numerous overfunded startups that lack adequate governance, leaving them to navigate the challenges of proving their worth and securing future funding rounds.
Evolving Role of Startup Scouts in the Innovation Ecosystem
In today’s rapidly evolving innovation landscape, startup scouts, also known as innovation scouts, have become indispensable players, bridging the gap between emerging startups and established organizations. Their role extends beyond identifying startups and is critical in nurturing the innovation pipeline that fuels growth and competitiveness. Some of the roles in the innovation landscape are:
- Spotting Disruptive Technologies and Trends: One of the primary responsibilities of startup scouts is to identify emerging technologies that could disrupt industries. By monitoring startup ecosystems, attending industry events, and leveraging their networks, scouts ensure that their organizations remain at the forefront of innovation.
- Facilitating Strategic Partnerships: Scouts play a pivotal role in forming partnerships that accelerate innovation by connecting startups with established companies. These partnerships are crucial in open innovation, where organizations look beyond internal R&D for innovative ideas.
- Startup Evaluation and Due Diligence: Scouts thoroughly evaluate startups, assessing their market fit, scalability, and team strength. This due diligence process ensures that investments and partnerships align with organizational goals.
- Supporting Creativity and Talent Acquisition: Startups often bring fresh perspectives to problem-solving, injecting creativity into established organizations. Scouts play a role in integrating these new ideas, enhancing their companies’ overall innovation capacity. Additionally, they are instrumental in talent acquisition, identifying key individuals from startups who can contribute new skills and perspectives to their organizations.
- Managing the Innovation Pipeline: Startup scouts consistently flow new ideas and technologies into their organizations. By proactively managing this pipeline, they help maintain a competitive edge and foster a culture of continuous innovation.
Opportunities and Considerations for Various Stakeholders
Startup scouting presents opportunities and considerations for various stakeholders, including Corporations, Startups, Investors, Governments, and Universities:
Opportunities:
- For Corporations: Partnering with startups offers access to innovative technologies and business models, enabling corporations to stay competitive and accelerate product development. By integrating startup solutions, corporations can enhance operational efficiencies and disrupt existing markets, positioning themselves as leaders in industry innovation.
- For Startups: Scouting can give startups access to capital, industry expertise, and expanded market reach through partnerships with established corporations. Such collaborations increase a startup’s visibility, credibility, and growth potential, enabling accelerated development and scaling through valuable resources and mentorship.
- For Investors: Scouting startups allows investors to discover high-growth potential opportunities with disruptive technologies and innovative business models. By diversifying their portfolios with high-risk, high-reward startups, investors can achieve significant returns from successful ventures and capitalize on emerging market trends.
- For Governments and Universities: Supporting startup ecosystems can drive local economic growth and foster innovation through research and development partnerships. Collaboration with startups enhances educational and entrepreneurial opportunities, contributing to a dynamic innovation landscape and addressing regional economic and technological challenges.
Considerations:
- For Corporations: Integration with startups can present challenges, including aligning the startup’s agile culture with the corporation’s structured processes and managing potential resistance to new ideas. Successful collaboration requires careful management of these integration issues to ensure productive outcomes.
- For Startups: Startups must navigate potential power imbalances and ensure fair terms when partnering with corporations. Maintaining their entrepreneurial spirit and independence is crucial, as over-reliance on corporate partners can hinder innovation and disrupt their original vision.
- For Investors: The high-risk nature of startup investments necessitates thorough due diligence to mitigate market unpredictability. Investors must balance their portfolios to spread risk effectively, acknowledging that startup investments carry inherent risks, including high failure rates and market volatility.
- For Governments and Universities: Balancing support and regulation is essential to foster innovation while managing resource allocation effectively. Ensuring that public policies align with the needs of the startup ecosystem and addressing the challenges of maintaining productive partnerships are critical considerations in supporting startup growth.
Call-to-action
Startup Scouting is a challenging and time-consuming task. That’s why companies consult and use the expertise of scouting firms like GreyB to help them find relevant startups according to their need.
Scouting firm industry experts and their experience helps to create a search process that involves a tailored approach, including industry analysis, trend mapping, and a comprehensive evaluation of startup viability and strategic fit with 30+ parameters. Further, a combination of proprietary algorithms and expert insights is used to identify startups that are not only innovative but also align with companies’ specific business goals and challenges.
Get in a Call to Consult with our scouting experts by filling out the form below:
Authored by: Vipin Singh, Marketing