In 2022, Medtronic paid $10 million to Insulet Corporation in an infringement lawsuit over tracking-enabled insulin pumps. Such high-stake cases highlight a growing issue in the healthcare sector. As companies invest in automated drug delivery, smart storage, and digital monitoring, the risk of inadvertent infringement and legal disputes increases.
In August 2024, Auto-Injection Technologies LLC acquired 22 patents from Sanofi, covering drug delivery systems, medicament containers, and electronic health monitoring. The competitor threat analysis hints that companies developing similar technologies must now assess their risk exposure right from potential licensing obligations, assertion threats, or litigation.
Among the transferred patents, US11730879B2 stands out. This patent is for a smart medication storage system that uses sensors, computing devices, and automated inventory management.
There is a growing demand for tracking temperature-sensitive drugs, wireless prescription refills, and solutions for medication adherence. Many companies are working on similar innovations, even if they don’t realize the overlaps yet.
This is where the risk escalates.
Patent Summary and Threat Analysis: US11730879B2
US11730879B2 describes a computing device integrated with a storage assembly to manage medicament delivery devices. The system combines real-time tracking, automated inventory management, and digital alerts, making it a critical innovation in medication adherence and pharmacy automation.
Key Features and Their Legal Implications
| Feature | Function | Patent Risk & Infringement Threat |
| Medicament Monitoring | Detects and tracks stored medicament delivery devices using sensors (e.g., cameras, barcode scanners). | Companies using automated inventory tracking in smart storage systems risk infringement if their technology overlaps with these claims. |
| Display System | Shows medicament type, dosage, and expiry on a screen integrated into the storage assembly. | Any digital medication storage device providing in-unit display features may be subject to assertion risks. |
| Wireless Connectivity | Connects to the internet to track inventory and reorder medications when supply is low. | IoT-enabled smart medication storage solutions using automated refills could trigger licensing demands or litigation. |
| User Alerts | Sends reminders and updates via connected devices to ensure adherence. | Medication adherence platforms incorporating smart storage and notifications must evaluate their risk exposure. |
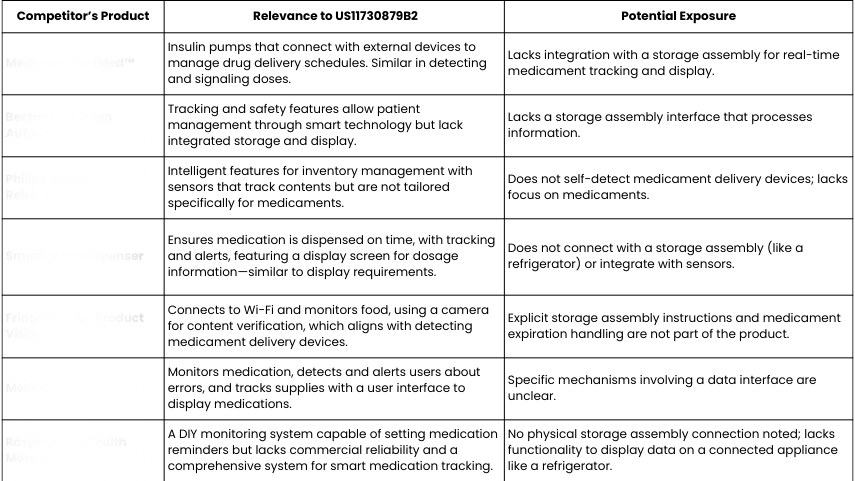
Competitive Patent Landscape: Overlapping Technologies in Medication Management
The following patents relate to automated medication dispensing, adherence tracking, and inventory management. While they share functional similarities, each patent varies in its scope and technical claims, making a detailed claim analysis essential for understanding market risks and potential conflicts.
| Patent | Abstract/Description | Key Functional Overlaps | Distinctive Technical Scope |
| US6XXXXXXB1 | The system for medicament delivery comprises a medicament container, dispensing mechanism, and electronic data management system for communication with a network. | Uses electronic data management systems for communication. | Focuses more on the delivery system rather than the storage assembly and direct interaction with monitoring devices. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | A system including a dispenser unit with a tray of medication canisters and a mobile computing device for monitoring adherence and dispensing. | Incorporates monitoring and adherence tracking of medication. | The dispensing device functionality is more prominent, lacking a direct connection to a storage assembly as per US11730879B2. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | System for dispensing medicaments that includes a processor, memory, and wireless communication to manage inventory. | Provides capabilities for inventory management of medicaments. | Does not focus on the specific interaction between a computing device and a storage assembly with display capabilities. |
| US3XXXXXXA1 | Medication dispensing device with containers for monitoring and controlling the dispensing process both locally and remotely. | Involves medication dispensing tied to monitoring and scheduling, similar to tracking dosages. | Emphasizes local and remote aspects of dispensing while not directly incorporating the storage assembly feature. |
| US4XXXXXXA1 | Includes mechanisms for dispensing medication and monitoring adherence using sensors to track the status of dispensing. | Contains mechanisms for tracking and dispensing medication. | Lacks the explicit connection to a storage assembly for monitoring multiple medicament delivery devices. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | A comprehensive pharmacy system that utilizes technology for managing medication regimes and dispensation schedules. | Utilizes technology for medication regime management and adherence tracking. | Less emphasis on smart storage and more on a pharmacy-centric approach rather than integrating storage elements. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | Method for operating a medicament dispenser with data communication for transmitting information about the medication. | Focuses on the dispensing of medicaments with data communication capabilities. | Does not explicitly mention interactivity with a storage device having a display for user information. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | A device combining a storage compartment with a communication facility for exchanging health data and presenting it to users. | Integrates a communication facility to exchange health data. | Primarily addresses a mobile phone application rather than a dedicated storage assembly with a connected computing device. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | A self-injection device with electronic tagging to monitor dosages and provide reminders for administration. | Self-injection device with tracking capabilities akin to the proposed monitoring in US11730879B2. | Primarily focused on self-injection without detailing a smart storage integration for disparate medicament storage. |
| US2XXXXXXA1 | A computer-based apparatus for storing and dispensing medications according to schedules, with real-time updates from a remote source. | Discusses dispensing medications with a computer-assisted approach for schedule adherence. | More concentrated on the dispensing method without the display and full integration with a storage assembly context. |
Patent Enforcement & Licensing Risk: US11730879B2 in the Market
While several companies have developed technologies related to US11730879B2, most do not yet fully align with the protected claims of the patent. However, as market adoption grows, these gaps may narrow, increasing the risk of infringement claims or licensing pressure.
Your Next Product Could Be at Risk!
While US11730879B2 is one of the tracked transactions, it represents just a fraction of how the automated medication management space is evolving. The challenge is not just knowing what has been acquired today but anticipating where the next critical patents will surface and how they will influence market positioning and enforcement trends.
The growing overlap in medication adherence tracking, smart storage, and inventory automation makes real-time competitive benchmarking essential. The companies shaping this space are not static, and neither is their IP strategy. Ensuring that each new filing, acquisition, or assertion is captured and analyzed in real-time is key to mitigating unexpected risks.
Slate provides a structured, real-time approach to competitive benchmarking, allowing organizations to track new entrants, monitor ongoing transactions, and map out portfolio shifts across key players.
Explore Slate’s power in streamlining your market entry strategies
Authored by: Ojasvi Jain and Rohit Sood, Patent Monetization Team