Did you know tech companies like Apple, IBM, Intel, and Qualcomm are filing patents in the tire domain?
No, I’m not kidding.
With the digital revolution and advancements in tech, your tire is no more a round piece of equipment that supports your vehicle and enables transit from one place to another. In the last few years, we have witnessed the opening of new horizons in a tire’s framework. This includes the development of embedded sensors in the tire, for–pressure regulation, road friction measurement, puncture detection, tread depth measurement, and several other techniques as a part of the tire health monitoring system.
In addition to sensors, we have also seen innovations like airless tires, connected tires (with a mobile device, nearby vehicles, network, or cloud), RFID-tagged tires, self-inflating wheels, run-flat (tires), and multiple other technologies being integrated with tires to digitalize fleet management and make the future of driving safer and smoother.
How digitalization has affected the tire industry?
Digitalization has created a whole different market segment outside the traditional tire industry via the infusion of technologies like 3D printing, organic raw material usage, tires for autonomous driving, airless tires, and integration of TPMS (tire pressure monitoring sensor), embedded chips, and self-inflation techniques. This new segment is being recognized as advanced or smart tires.
This advanced tire market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.98% in the upcoming 10 years.
The advanced tire sales are projected to grow from an estimated US $ 219.7 million in 2020 to a value of US $ 1,148.3 million by 2030 (Source).
Which other non-tire players are working in the smart tire domain?
This new development in the world of tires motivated many other players from non-tire domains to be a part of the tire industry’s revolution.
Multiple IT companies, 3D printing companies, Sensors and electronics OEMs, and companies working in the self-driving sector are viewing the tire industry as the market of the future.
We were curious to find out how many shares these companies hold in this niche. To find answers, we extracted a patent set related to smart/advanced tire systems on the Derwent patent database.
We found that more than 25% of the patents in the field have been filed by companies that don’t exactly operate in the core tire field. These included companies like Apple, Uber, Qualcomm, Samsung, Intel, Xiaomi, IBM, and so on.
From this long list of non-core companies, we hand-picked 4 major players and analyzed them further – Apple, IBM, Intel, and Qualcomm. We looked into their patents as well as the type of service/product they are offering, to get a better understanding of how they are conducting business in the domain of tires. Let us have a look.
1. Apple
Apple has been slowly revealing how its research, projects, and ambitions are not just limited to iPhone and iPad. If the dream and rumor of iCar or The Project Titan (as per the wall street journal) are true, Apple is expected to be tough competition for Tesla in the autonomous car market in upcoming years (Source).
As per Patently Apple, the firm owns about 90+ published patents (some applications, some grants) under Project Titan which comprises patents related to vehicle technology and autonomous driving. These patents are related to domains like – suspension, smart glasses in cars, 3D AR-based windshields, chassis control, airbags, safety belts, and much more exclusively for autonomous vehicles (Source).
Apple is also researching sensors to detect and calculate tire-road friction value and thereby, determining the lubricant needed. This is evident from its patent filing (US10773725B1). Another patent (US10247816B1) granted to Apple, suggests the placement of a pair of sensors at the bottom of the vehicle to generate a pair of “Doppler Slopes” of signal and determine relative velocity, and ground vehicle angle. This can further be used to calculate relative sliding (slip) at the tire-road interface.
How are these patents going to contribute to Apple’s driverless fleet mission?
In a 2017’s Bloomberg interview, Apple’s CEO Tim Cook suggested that Apple is working on an autonomous driving platform. Certain acquisitions, investments in self-driving technology, and even the hiring of ex-Tesla employees by Apple suggested its interest in entering into the autonomous vehicle industry (Source).
Interestingly, Elon Musk claimed that he offered Apple to acquire Tesla in 2017, and was turned down.
We believe that reason behind not acquiring Tesla at that time was – Apple’s M&A policies are always inclined more towards unique talent or technology rather than just brand, revenue, and user base (Source).
Let us have a look at more of such acquisitions, collaborations, and news in the area for Apple.

Apple hired Michael Schwekutsch (Tesla’s former vice president in charge of drive systems) in 2019, Stuart Bowers (Tesla’s former vice president) in 2020, and Jonathan Sive (vehicle engineer from BMW AG, Tesla, and Alphabet) for its autonomous car’s project. Elon Musk referred to Apple as Tesla’s graveyard as per a report.
Expected partners for Apple’s Project Titan are Foxconn, Magna, Hyundai (and its affiliate Kia), Nissan, and Stellantis, and it is also open to partnering with other OEMs from similar backgrounds (Source).
2. International Business Machines (IBM)
IBM is one of the topmost patent filers that provide solutions, consulting, software, and several other services to companies of multiple domains.
After the evolution of autonomous driving, manufacturers are either shifting to connected vehicles or integrating digital solutions to enhance products, operations, and customer engagement in Tire industries (Source).
IBM is researching sensors, techniques, and programs for the measurement of tire pressure, as well as tire inflation and deflation rate. This is evident from the patents US10455185B2 and US8615344B2, granted to IBM.
Are there any products or services offered by IBM, where it is deploying these innovations?
For this, we explored a few services and solutions offered by IBM which were either exclusively for or were complementing the tire industry in some other way. Those are –
- Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) solution: ELM (7.0) integrates development processes such as OSLC, SAFe 4.6, and Agile interoperability and uses AI to augment system requirements as per automotive standards (Source).
- IBM IoT connected vehicle insights: It is a connected car software that acquires data from sensors embedded in tires (such as tire pressure sensors, puncture detection sensors, and so on), and systems to provide useful insights (Source).
- IBM Maximo software for transportation: It offers certain digital features in its software for wheel validation and altering tire’s axle configuration by rotating it as per the need (Source1 and Source2).
Besides, IBM offers Maximo visual inspection for error-proof automotive production (Source); IBM iX – AI-powered customer engagement solutions to accelerate automotive sales (Source); solutions to cut, transform, and modernize automotive business in collaboration with SAP (Source); and a few more. IBM also provides X-Force red automotive testing platform based on IoT and other recent technologies (Source).
What are some popular clients and partners of IBM in the context of the above-mentioned automotive technologies?
 | Continental collaborated with IBM in 2013, to integrate big data and cloud-based solutions for fully connected vehicles with advanced mobility. The aim of this collaboration was that continental was about to deliver a range of new mobile-based in-car services (Source). |
 | Volkswagen collaborated with IBM to utilize IBM garage’s design and DevOps methodologies into its business, development, design, and observation of data derived from the cars (Source). |
 | IBM signed a US $ 1.3 billion, 8-year outsourcing deal with Michelin under which IBM managed IT infrastructure, production, operations and management, user support, technical support, servers, workstations, PCs, software, and production applications for Michelin (Source). |
 | BMW partnered with IBM to integrate IBM’s Bluemix platform into its CarData network. This was done to use cloud computing in the connected vehicle for diagnosing and repairing problems, save on car insurance and use third-party services (Source). |
Along with this, IBM also partnered with other major companies such as – General Motors, Honda, Mitsubishi, Daimler AG, and Bell Tire.
3. Intel
Intel is the world’s largest semiconductor chip manufacturer based on revenue (Source). Intel remained one of the biggest stakeholders in the self-driving car industry, having joined the race in mid-2017, after joining forces with Mobileye (Source).
After a solid start in the automobile industry, Intel leads a series of acquisitions, patent filings, manufacturing, and deployments to establish its position in the sector.
Intel is currently researching a friction-measuring model that includes a sensor interface, a predictive model, and a communication interface that can transmit the friction value and alert the driver about upcoming hazards. This is evident from its two recent patent applications – US20200223443A1 and US20200255021A1
Are there any products and collaborations based on the following patents?
Intel’s technology, along with Capgemini’s solution service and Google Cloud’s platform, created an AI-driven Personalized Voice Assistant (PVA) that uses natural language processing to recommend service centers, advice on distance, journey time, opening hours, and services such as – new tire fittings, tire rotation and balancing, flat repairs, and winter tire changes.
Intel’s intelligent sensors along with Shanghai-based DeepSight developed a system for detecting defects in tire manufacturing. This arrangement uses intel’s industrial computer and sensor; DeepSight’s deep inspection for defect analysis, and Intel’s OpenVINO toolkit for complete detection, analysis, and communication back of alerts for defects through the same production line (Source).
BMW partnered with Intel and its acquired AI-based unit Mobileye in 2016 with the resolution of collaborating the expertise of automotive technologies, computer vision, and machine learning, and producing fully autonomous fleet solutions in form of BMW’s iNEXT autonomous car, which is supposed to launch by 2021 (Source).
As the news of Germany-based automobile giant BMW’s collaboration with Mobileye and semiconductor giant intel spread over the industry, many other big names such as the US’ top automobile company Fiat, joined forces with them in 2017, and many companies will continue to do so in upcoming years.
4. Qualcomm
Qualcomm, one of the largest patent filers in the world, as well as the assignee of critical CDMA patents, has been trying to conquer the domain of connected and smart vehicles (Source).
Telematics is the combination of telecommunication, vehicular, electrical, and computer science, and it gained momentum after the evolution of autonomous vehicles (Source). Technologies like V2X (vehicle-to-everything), TPMS (tire pressure monitoring sensors), and the integration of several other microcontrollers and chipsets in tires have opened the ground for a wireless-technology giant like Qualcomm to expand its market in Tire Industry.
Qualcomm researched a multipoint wireless broadcast system, as well as the use of a transducer to detect tire failure and provide an alert to the driver beforehand. This is evident from its patent (EP2954730A1 and WO2008011470A1) filings as well.
Let us have a look at a few products by Qualcomm, which shows its interest in the world of tires, autonomous, and connected vehicles –

- Qualcomm’s QCA6595AU Wi-Fi 5 / BT5.1 Automotive Dual-MAC Combo Chip is the most advanced Wi-Fi 5/ BT 5.1 combo chip in the Automotive Infotainment and Telematics markets. Its applications include wireless car projection in phones, multiple wireless cameras, low-latency, and long-range TPMS (tire pressure monitoring system) applications, and much more (Source).
- Launched in January 2020, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon ride platform is one of the most advanced, customized, and scalable ADAS (Advanced driver-assistance system) in the automotive industry currently (Source).
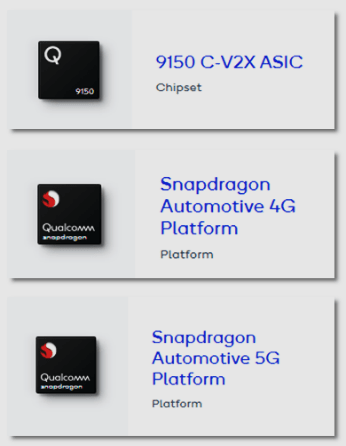 | Snapdragon 820 was the first chip of the series that deployed LTE-based V2X (vehicle-to-everything) technology for connected cars. The 4G version was an updated multimode LTE modem with integrated C-V2X. The 5G upgrade was a 3GPP’s Release 15-based 5G multimode modem supporting 5G, LTE, 3G, and 2G with C-V2X, DSDA, and several other automotive services. |
Several other chipsets, processors, and platforms were developed by Qualcomm to supplement the revolutionizing automobile industry. Besides, Qualcomm also collaborated with several automobile companies for the implementation and commercialization of its chipsets and technologies.
Let us have a look at some major collaborations concerning these products and patents –
 | In August 2000, Qualcomm partnered with Ford Motors under the banner-name of “Wingcast” to incorporate internet and intelligence into cars (Source). This joint venture was dissolved in 2002 due to the varying perspectives of both companies. |
- Qualcomm made numerous partners to advance in the domain of telematics, V2X (vehicle-to-everything), and wireless car connectivity in recent years. Some of the major partners include Mercedes AMG, LG, ZTE, Continental, General Motors, and so on (Source1 and Source2).
- In the European space, some major clients of Qualcomm using its V2X chipsets are Savari, commsignia, ficosa, Quectel, Cohda, Neusoft, Telit, Sasken, Danlaw, and so on.
Concluding Notes
The list of automobile OEMs collaborating with Qualcomm, Apple, Intel, and IBM, is never-ending. Speaking of advanced tires, it would be interesting to see how big digital companies and new tech start-ups take advantage of the growing tire demand.
Another important thing to notice is that the cloud plays a vital role in the autonomous industry. It would be interesting to see how cloud giants like AWS, Google, Microsoft Azure, and several others compete and enhance their business and services in the connected vehicle domain, and who makes the maximum fortune out of it.
In addition to acquiring edge, cloud, and AI-based companies, tire giants like Bridgestone, Goodyear, Michelin, or Pirelli might also start in-house research in the future and form technical units to keep in pace with embedded and AI-based technologies for a tire.
The smart tire industry is growing at a fast pace with a ton of R&D happening in almost all the areas of the niche. If you are working in the advanced tire domain, a technology landscape analysis of the same would help you design effective attack and defensive strategies against other competitors in the domain. Want to discuss the deets?

Authored by: Sarvagya Saxena, Intelligence Team.